Ductus diverticulum
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Andrea Molinari had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Andrea Molinari's current disclosures- Aortic ductus diverticulum
- Ductus bump
- Ductus diverticula
- Ductus bumps
- Aortic ductus diverticula
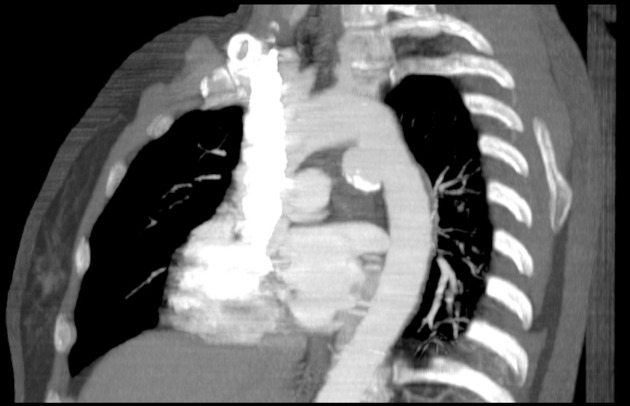
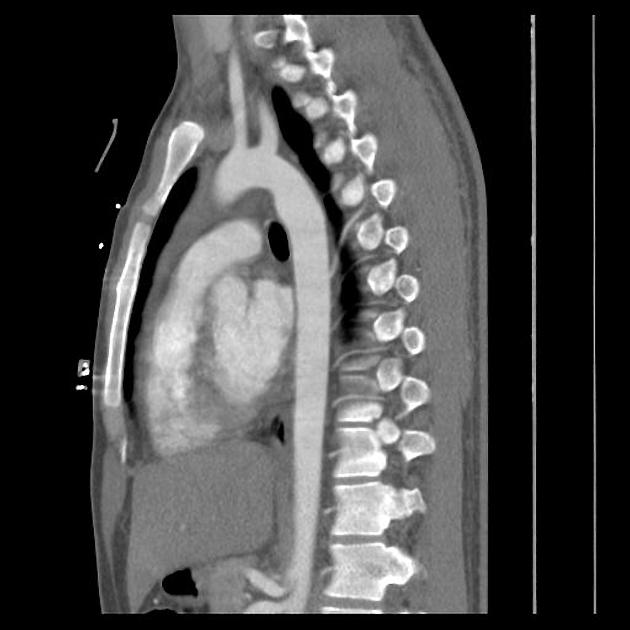
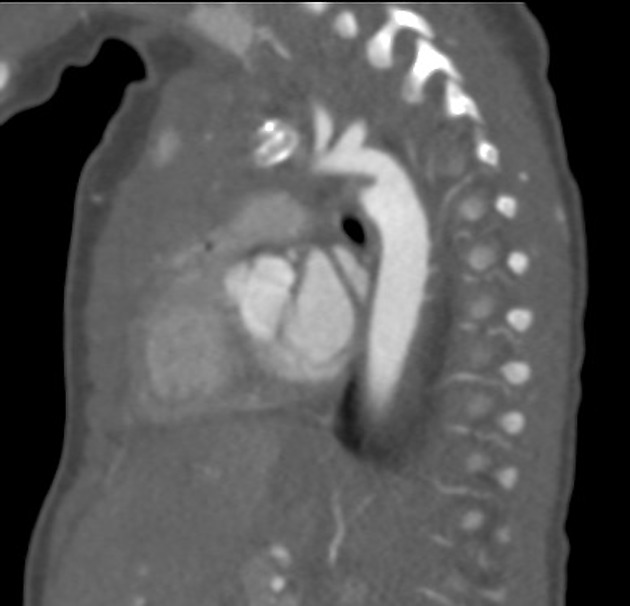
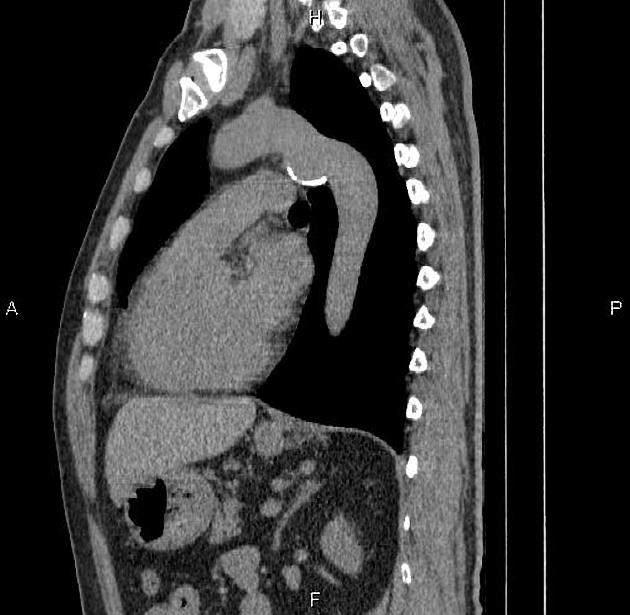
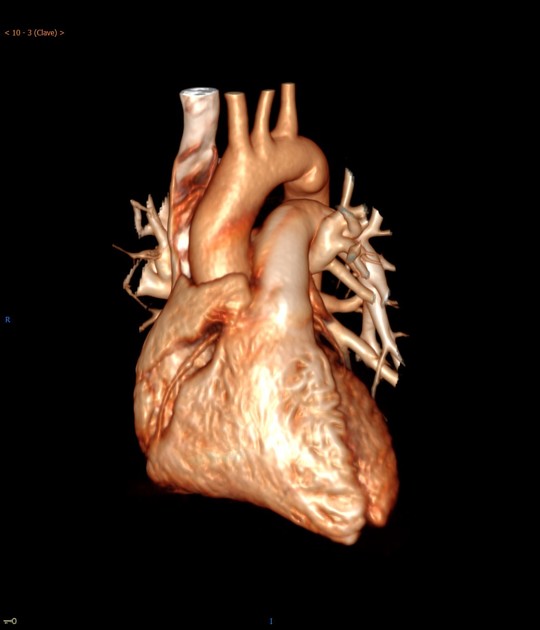
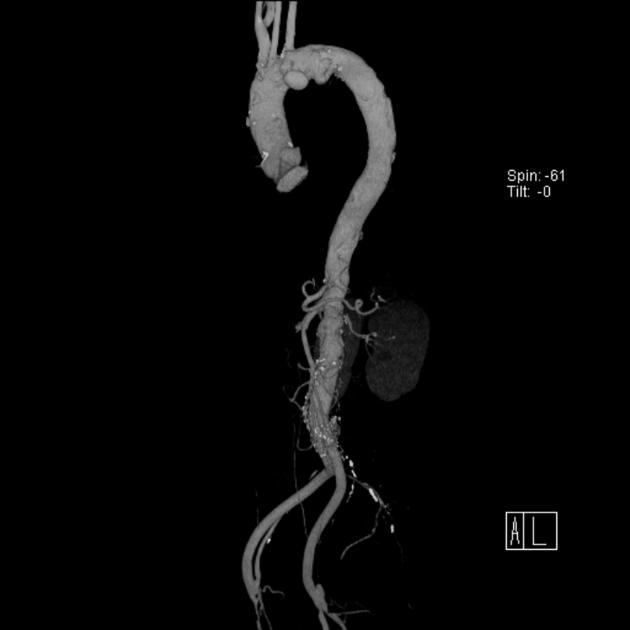
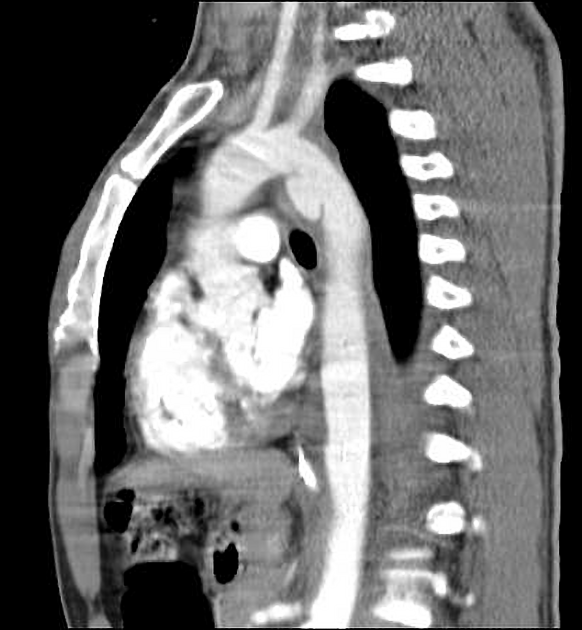
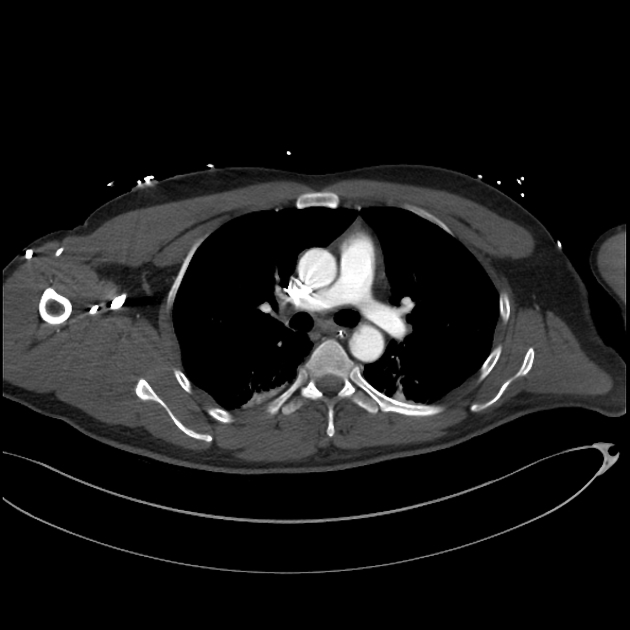
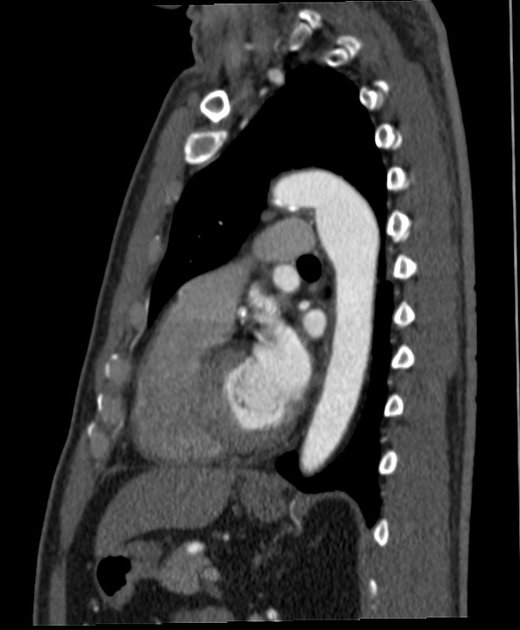
Aortic ductus diverticulum is a developmental outpouching of the thoracic aorta which may be mistaken for an acute aortic injury.
Gross anatomy
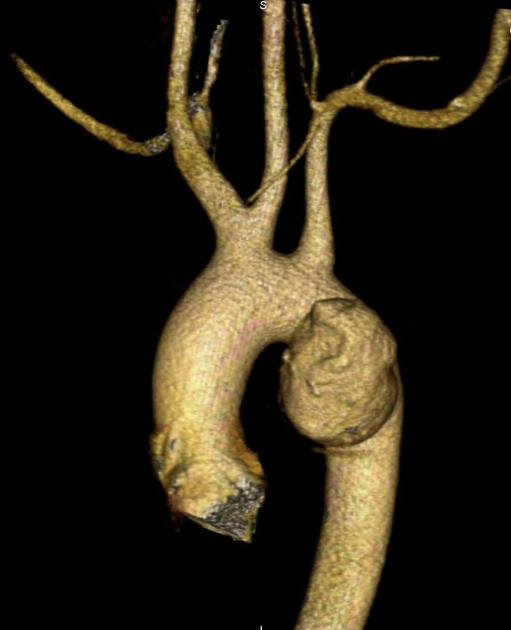
It is usually seen at the anteromedial aspect of the aorta at the site of the aortic isthmus, where the ligamentum arteriosum attaches. It is also the site of the majority (~90%) of post-traumatic aortic injuries as the ligamentum arteriosum is one of the points to which the thoracic aorta is tethered; therefore, differentiation of ductus diverticulum from traumatic pseudoaneurysm is vitally important.
In contrast to an aortic pseudoaneurysm, which usually forms sharp margins with the aorta, the ductus diverticulum usually appears as a smooth focal bulge with gentle obtuse angles with the aortic wall.
Types
Ductus diverticula are divided into:
-
classic
smooth gentle shoulders
33% newborns
9% adults
-
atypical
sharper with a shorter and steeper superior slope
Differential diagnosis
aortic spindle - circumferential dilatation just distal to the isthmus
descending aortic diverticulum - due to an incomplete double aortic arch
For differentiating features, see aortic pseudoaneursym versus ductus diverticulum.
References
- 1. Batra P, Bigoni B, Manning J et al. Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Thoracic Aortic Dissection at CT Angiography. Radiographics. 2000;20(2):309-20. doi:10.1148/radiographics.20.2.g00mc04309 - Pubmed
- 2. Goodman P, Jeffrey R, Minagi H, Federle M, Thomas A. Angiographic Evaluation of the Ductus Diverticulum. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1982;5(1):1-4. doi:10.1007/BF02552093 - Pubmed
- 3. Grollman J. The Aortic Diverticulum: A Remnant of the Partially Involuted Dorsal Aortic Root. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1989;12(1):14-7. doi:10.1007/BF02577119 - Pubmed
- 4. Ferrera P & Ghaemmaghami P. Ductus Diverticulum Interpreted as Traumatic Aortic Injury. Am J Emerg Med. 1997;15(4):371-2. doi:10.1016/s0735-6757(97)90128-5 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Stanford type B aortic dissection
- Ductus diverticulum
- Epithelioid mesothelioma
- Diaphragmatic rupture and ductus diverticulum
- Incomplete double aortic arch
- Large ductus diverticulum or ductus arteriosus aneurysm
- Multitrauma: intracranial, spinal, thoracic and pelvic injuries
- Traumatic aortic injury and bowel injury
- Ductus diverticulum
- Ductus arteriosus aneurysm
- Ductus diverticulum
- Aortic ductus diverticulum
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax
- thoracic viscera
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax
- innervation of the thorax
Related articles: Pathology: Vascular: Aortic
- acute aortic syndrome
- aortic aneurysms
- inflammatory
- congenital
- aortic coarctation
- aortic pseudocoarctation
- cervical aortic arch
- interrupted aortic arch
- transposition of the great arteries
- variant anatomy of the aortic arch
- traumatic aortic injury
- miscellaneous




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.