Epidural lipomatosis
Updates to Article Attributes
Epidural lipomatosis refers to an excessive accumulation of fat within the spinal epidural space, such that the thecal sac is compressed.
Clinical presentation
Patients may present with back pain resembling that of a disc herniation. In severe cases, symptoms of canal stenosis are produced.
Pathology
Characterizedby the abnormal accumulation of unencapsulated adipose tissue in in the extradural space.
Causes
- obesity
- Cushing disease
- Cushing syndrome: most frequently due to corticosteroid use
- prolactinoma
Location
Typically involves the lower lumbar and/or lower thoracic levels.
Radiographic features
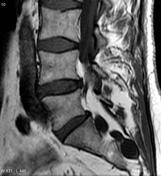
MRI spine
There is aan often generalised excess of fat seen in the extradural space. As a result, the dural sac can appear narrowed or even resemble a "Y" shaped configuration.
Signal characteristics follow fat on all sequences:
- T1: high signal
- T1 (FS): shows fat suppression
- T2: high signal
-<p><strong>Epidural lipomatosis </strong>refers to excessive accumulation of fat within the <a title="Spinal epidural space" href="/articles/spinal-epidural-space">spinal epidural space</a>, such that the <a title="thecal sac" href="/articles/thecal-sac">thecal sac</a> is compressed.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Patients may present with back pain resembling that of a <a href="/articles/disc-herniation">disc herniation</a>. In severe cases, symptoms of canal stenosis are produced.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>Characterized<sup> </sup>by the abnormal accumulation of unencapsulated adipose tissue in the extradural space.</p><h5>Causes</h5><ul>- +<p><strong>Epidural lipomatosis </strong>refers to an excessive accumulation of fat within the <a href="/articles/spinal-epidural-space">spinal epidural space</a>, such that the <a href="/articles/thecal-sac">thecal sac</a> is compressed.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Patients may present with back pain resembling that of a <a href="/articles/disc-herniation">disc herniation</a>. In severe cases, symptoms of canal stenosis are produced.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>Characterized<sup> </sup>by the abnormal accumulation of unencapsulated adipose tissue in the extradural space.</p><h5>Causes</h5><ul>
-</ul><h5>Location</h5><p>Typically involves the lower lumbar and/or lower thoracic levels.</p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>MRI spine</h5><p>There is a often generalised excess of fat seen in the extradural space. As a result the dural sac can appear narrowed or even resemble a "Y" shaped configuration.</p><p>Signal characteristics follow fat on all sequences:</p><ul>- +</ul><h5>Location</h5><p>Typically involves the lower lumbar and/or lower thoracic levels.</p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>MRI spine</h5><p>There is an often generalised excess of fat seen in the extradural space. As a result, the dural sac can appear narrowed or even resemble a "Y" shaped configuration.</p><p>Signal characteristics follow fat on all sequences:</p><ul>
Image 1 Annotated image (AXIAL T2) ( create )
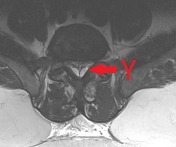
Image 2 MRI (T1) ( update )

Image 3 MRI (T1) ( update )
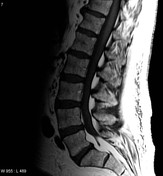
Image 4 MRI (T1) ( update )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.