Exencephaly is a lethal congenital fetal brain developmental anomaly (neural tube defect) considered to be a precursor to anencephaly in the acrania-exencephaly-anencephaly sequence.
On this page:
Pathology
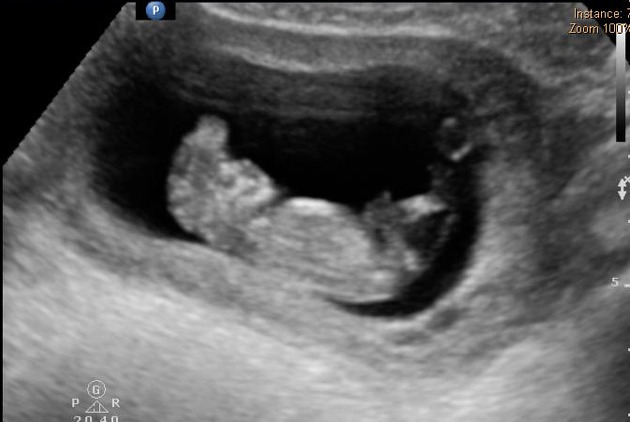
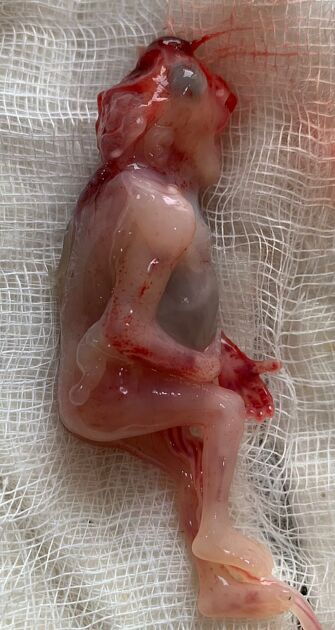
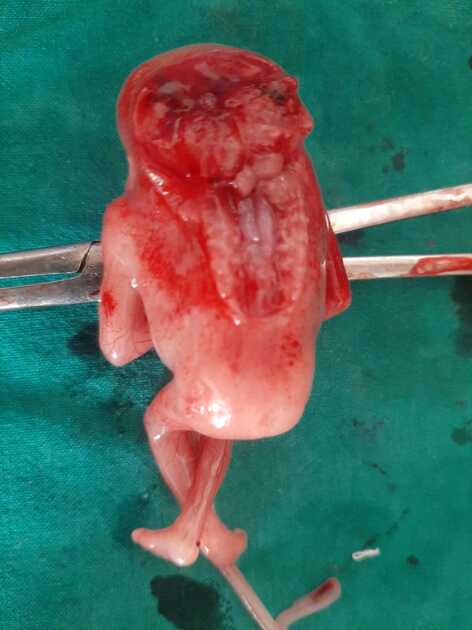
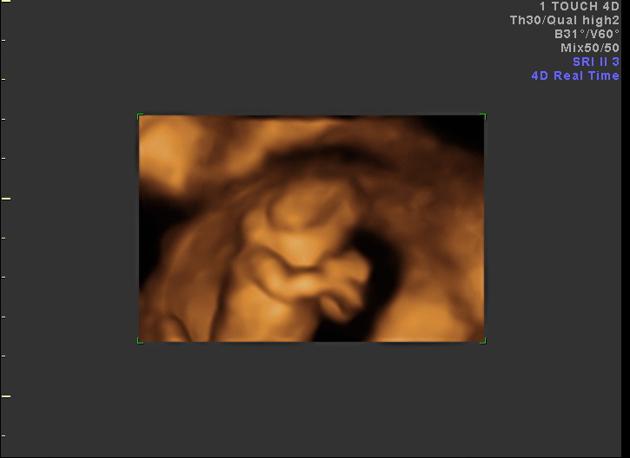
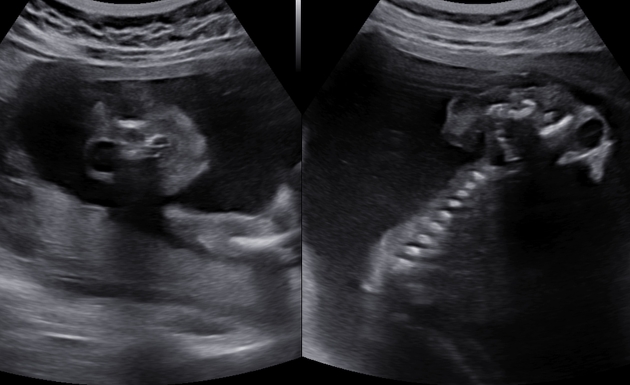
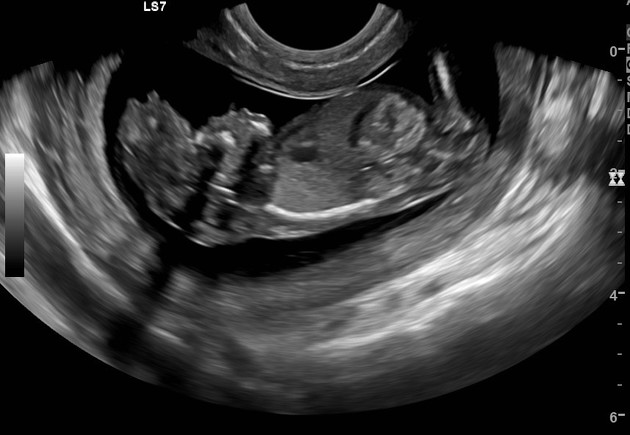
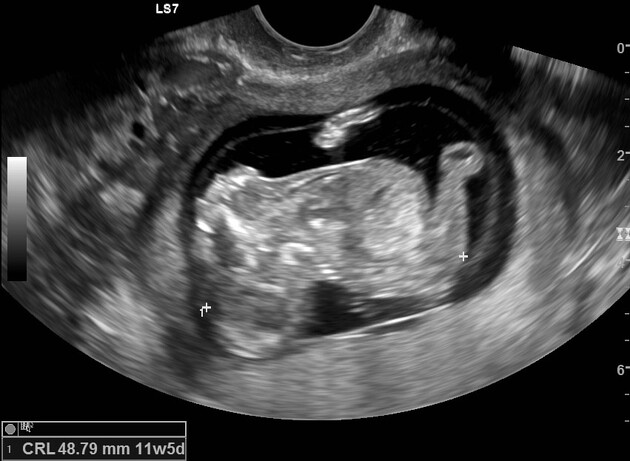
It is characterized by calvarial absence and loss of fetal brain tissue to variable degrees and is considered a precursor to anencephaly 3 in the acrania-exencephaly-anencephaly sequence.
Markers
- maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) levels are highly elevated (x 2.5 MoM)
Radiographic features
Imaging features have some overlap with that of anencephaly except that there is some brain tissue presence:
- cranial vault is absent or poorly formed, cephalad to orbits
- the nasal bone may be absent in most cases
- brain tissue is herniating or dangling in amniotic fluid
- brain tissue may be attached to the amniotic membrane
Treatment and prognosis
Exencephaly is a precursor to anencephaly, and essentially a fatal condition. Depending on local laws, advice and counseling for abortion are to be given to the parents.
See also
- acrania: calvarial absence but almost all brain tissue present
- anencephaly: absence of calvarium as well as brain tissue





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.