Urinary bladder diverticulum
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Ian Bickle had no recorded disclosures.
View Ian Bickle's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ammar Ashraf had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ammar Ashraf's current disclosures- Bladder diverticulum
- Urinary bladder diverticula
- Urinary bladder diverticulae
- Urinary bladder diverticuli
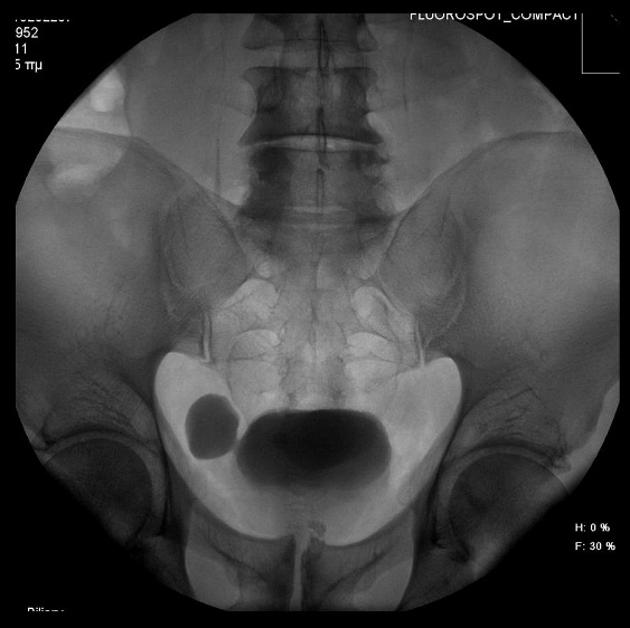
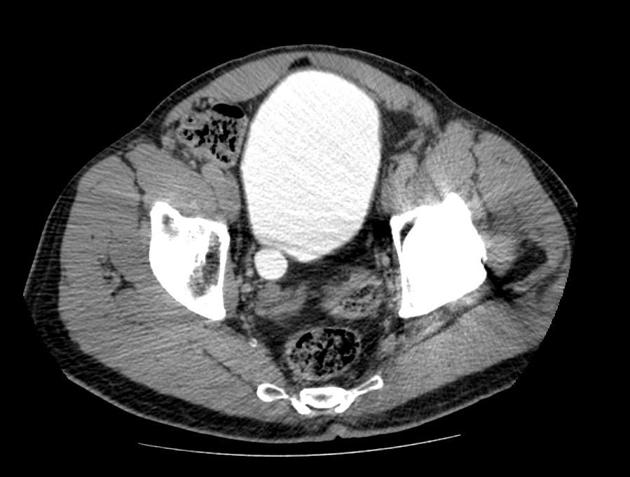
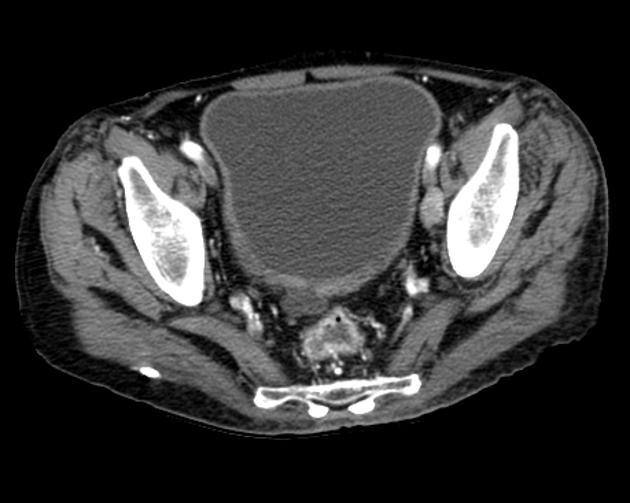
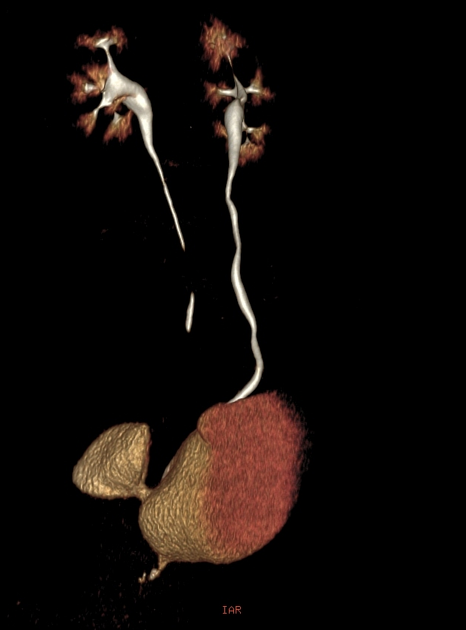
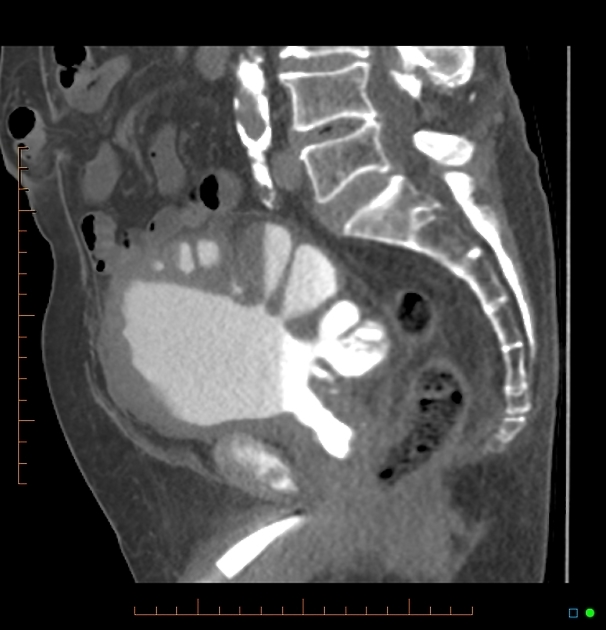
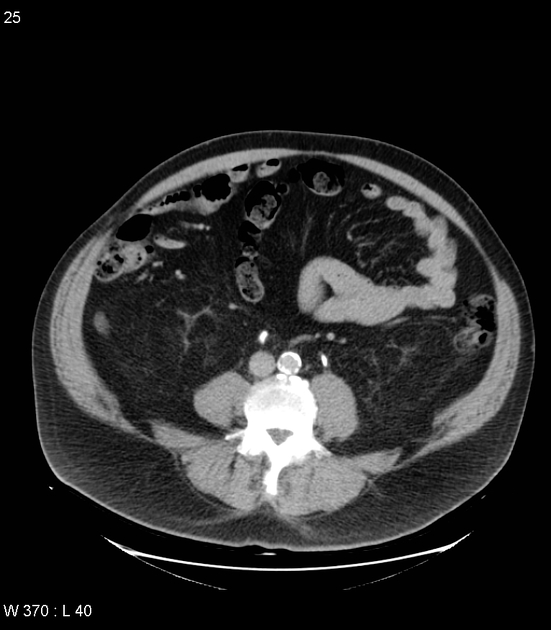
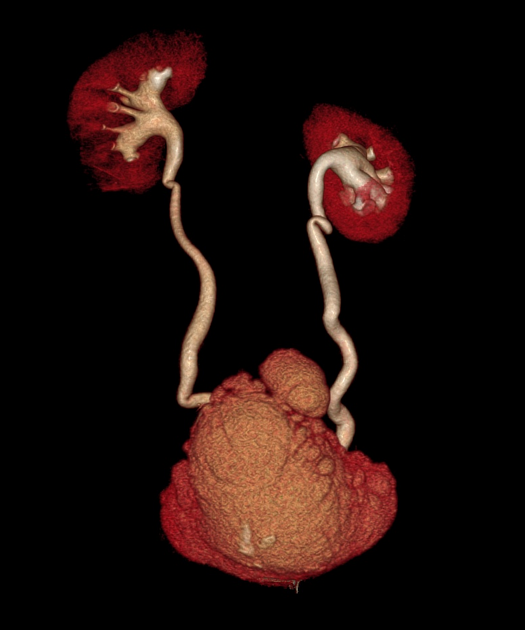
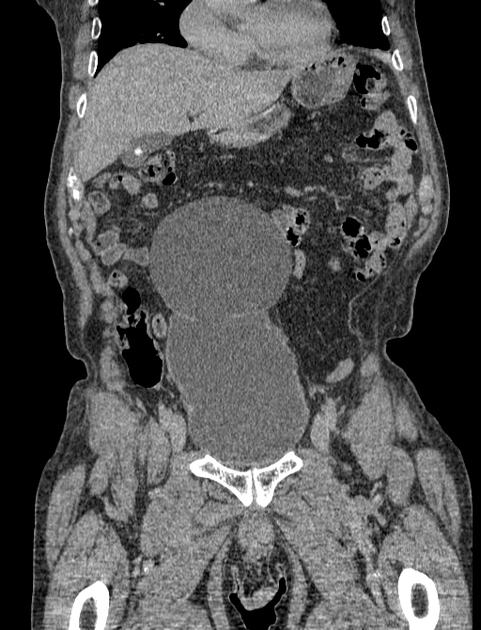
A urinary bladder diverticulum (plural: diverticula) is an outpouching from the bladder wall, whereby mucosa herniates through the bladder wall. It may be solitary or multiple in nature and can vary considerably in size.
On this page:
Epidemiology
There are two peaks; one at 10 years and the other at 60-70 years 2.
Pathology
Diverticula may be congenital (primary) or acquired (secondary) and a range of causes of urinary bladder diverticula are described.
Acquired diverticula are more common, usually occurring in the context of a trabeculated bladder, resulting from chronic bladder outlet obstruction.
While normal intravesical pressure is approximately 30cm of water at the commencement of micturition, 2-4 times this pressure may be achieved by a hypertrophied (trabeculated) bladder in an attempt to overcome outlet obstruction 9. This increase in pressure forces mucosa between superficial muscle bundles causing small pockets or cellules to form 9.
If these cellules are forced entirely through the muscular layer of the bladder they form saccules and then finally diverticula. It is important to note these diverticula contain no muscular wall and therefore cannot effectively expel their contents regardless of whether obstruction is relieved 9.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Radiographic features
Diverticula are often an incidental finding on imaging investigations, including ultrasound, CT, MRI and IVU.
Treatment and prognosis
Complications
They may be associated with a range of complications due to stasis and low-grade infection including:
intradiverticular transitional cell carcinoma 1-10% 5-7
References
- 1. Berrocal T, López-Pereira P, Arjonilla A, Gutiérrez J. Anomalies of the Distal Ureter, Bladder, and Urethra in Children: Embryologic, Radiologic, and Pathologic Features. Radiographics. 2002;22(5):1139-64. doi:10.1148/radiographics.22.5.g02se101139 - Pubmed
- 2. Erich Lang. Radiology of the Lower Urinary Tract. (2011) ISBN: 9783642844331 - Google Books
- 3. Shailendra Chopra. Genitourinary Imaging. (2011) ISBN: 9781604063240 - Google Books
- 4. Walker N, Gan C, Olsburgh J, Khan M. Diagnosis and Management of Intradiverticular Bladder Tumours. Nat Rev Urol. 2014;11(7):383-90. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2014.131 - Pubmed
- 5. Melekos M, Asbach H, Barbalias G. Vesical Diverticula: Etiology, Diagnosis, Tumorigenesis, and Treatment. Urology. 1987;30(5):453-7. doi:10.1016/0090-4295(87)90378-5 - Pubmed
- 6. Matta E, Kenney A, Barré G, Vanlangendonck R. Intradiverticular Bladder Carcinoma. Radiographics. 2005;25(5):1397-403. doi:10.1148/rg.255045205 - Pubmed
- 7. Golijanin D, Yossepowitch O, Beck S, Sogani P, Dalbagni G. Carcinoma in a Bladder Diverticulum: Presentation and Treatment Outcome. J Urol. 2003;170(5):1761-4. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000091800.15071.52 - Pubmed
- 9. Jack W. McAninch, Tom F. Lue. Smith and Tanagho's General Urology, 19th Edition. (2020) ISBN: 9781259834332 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Occipital horn syndrome
- Drug-induced renal calculi
- Hutch diverticulum
- Diverticular disease
- Prostatomegaly
- Urachal cyst
- Urinary bladder trauma
- Urinary bladder cyst
- Posterior urethral valves
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Menkes disease
- Urinary bladder diverticula (causes)
- Ureterocele
- Transitional cell carcinoma (urinary bladder)
- Cystitis
- Bladder calculus
- Seminal vesicle cyst
- Urinary bladder
- Ectopic ureter
- Urinary bladder diverticulum transitional cell carcinoma
- Bladder diverticula due to prostate enlargement
- Urinary bladder diverticulum
- Hutch diverticulum
- Posterior urethral valves
- Giant urinary bladder diverticulum
- Hutch diverticulum
- Urethral diverticulum
- Hutch diverticula
- Obstructive ileocecal adenocarcinoma
- Undifferentiated carcinoma of the pancreas
- Urinary bladder diverticulum
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Urinary bladder diverticula
- Urinary bladder diverticulum
- Urinary bladder diverticulum
- Urinary bladder diverticula
- Gallstone ileus
- Bladder diverticula
- Posterior urethral valve with grade V vesico-ureteric reflux
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.