Presentation
Past history of a ruptured ovarian cyst. Severe right lower abdominal pain.
Patient Data
Transabdominal US of the pelvis including the right iliac fossa was normal, therefore transvaginal imaging was performed.
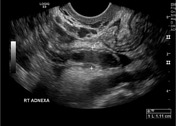
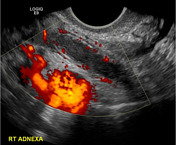
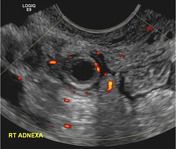
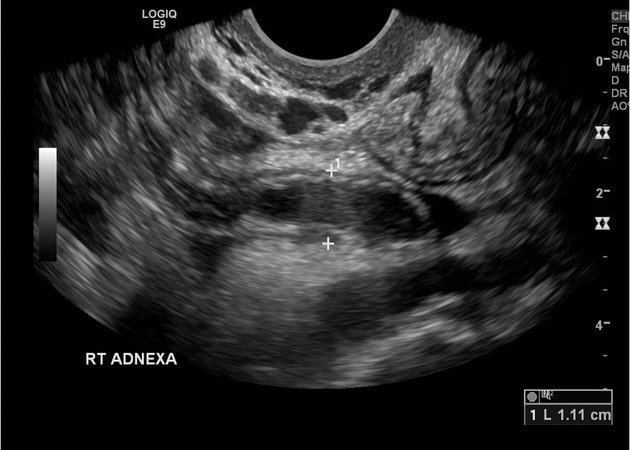
Right adnexal tender, fluid-filled, blind-ending tubular mass with surrounding free fluid. Increased blood flow in the wall of the tubular structure adjacent to iliac vessels.
Case Discussion
Despite this being a transvaginal examination, appearances are all consistent with acute appendicitis. Differential diagnosis is acute salpingitis but the tubular structure is blind-ending and not associated with the ovary.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.