Presentation
Vomiting, right upper quadrant pain and altered blood tests.
Patient Data
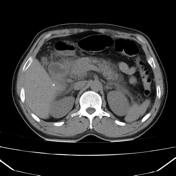



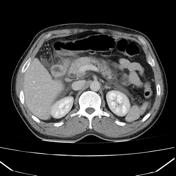

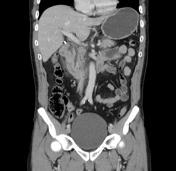

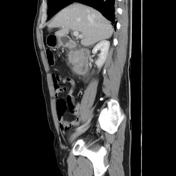

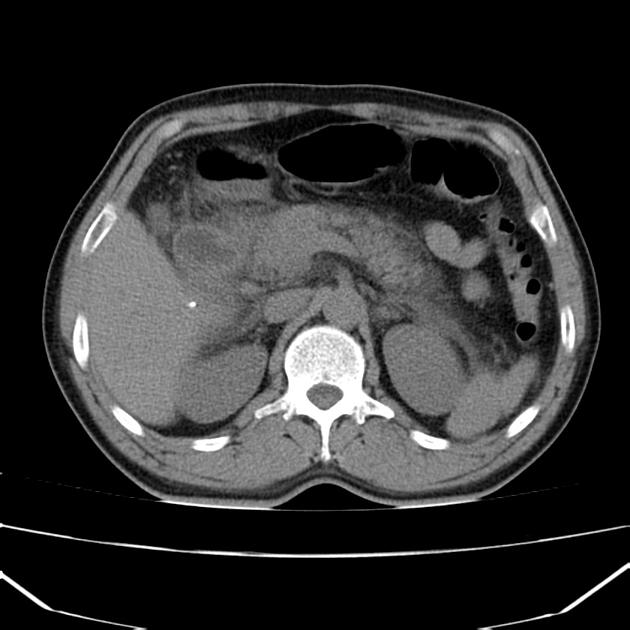
CT shows normal glandular pancreatic enhancement and diffuse appearance with peripancreatic inflammatory fat stranding and low attenuation retroperitoneal fluid surrounding the pancreas and extending into the duodenal portions. Absence of gallbladder (surgical history), in the gallbladder bed with post-cholecystectomy clips. Dilatation of the extra-hepatic bile duct. Gallstones are not observed on this imaging modality. The liver, spleen, adrenals and right kidney are within normal limits.
Case Discussion
Features consistent of acute pancreatitis.
The role of CT in the context of an acute pancreatitis are confirming the clinical diagnosis and most importantly evaluate possible complications such as; necrosis, hemorrhage, infection, or vascular complications (such as a pseudoaneurysm) and intra or peripancreatic collections. As in this case CT serves to demonstrate the existence of peripancreatic edema and necrosis absence which would change the clinical setting.
The timing of imaging is important. Traditionally post 72 hours from the presentation was advised, but some evidence and institutions image with CT after 48 hours.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.