Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Updates to Link Attributes
Updates to Article Attributes
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) (also known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis or Still's disease) is the most common chronic arthritic disease of childhood, and has multiple subtypes.
Epidemiology
The estimated incidence is around 6-20 per 100000 per annum 3.
Clinical presentation
Oligoarticular or polyarticular arthritis of a duration of six weeks or longer must be present to diagnose JIA.
Patients may present with an acute onset of symptoms or a more gradual onset. Symptoms are often worse in the morning, but typically persist to some extent throughout the day.
In patients with systemic onset, intermittent spiking fevers are typically noted, which help distinguish JIA from other diseases such as infection, other inflammatory diseases and malignancy. A light pink rash involving the trunk and/or extremities is also frequently observed in patients with systemic onset.
Radiographic features
Imaging shows a varied spectrum of involvement, based on the severity and duration of the disease.
Plain film
Findings on x-ray include soft tissue swelling, osteopenia, loss of joint space, erosions, growth disturbances (epiphyseal overgrowth) and joint subluxation.
Hepatosplenomegaly may be seen on abdominal radiographs, and pericardial or pleural effusions may be seen on chest radiographs.
MRI
MRI shows synovial hypertrophy, joint effusions as well as osseous and cartilaginous erosions. Active synovitis is characterized by enhancement on T1-weighted gadolinium contrast studies.
-<p><strong>Juvenile idiopathic arthritis </strong>(<strong>JIA</strong>) (also known as <strong>juvenile rheumatoid arthritis</strong> or <strong>Still's disease</strong>) is the most common chronic arthritic disease of childhood, and has multiple subtypes.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Oligoarticular or polyarticular arthritis of a duration of six weeks or longer must be present to diagnose JIA.</p><p>Patients may present with an acute onset of symptoms or a more gradual onset. Symptoms are often worse in the morning, but typically persist to some extent throughout the day.</p><p>In patients with systemic onset, intermittent spiking fevers are typically noted, which help distinguish JIA from other diseases such as infection, other inflammatory diseases and malignancy. A light pink rash involving the trunk and/or extremities is also frequently observed in patients with systemic onset.</p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><p>Imaging shows a varied spectrum of involvement, based on the severity and duration of the disease.</p><h5>Plain film</h5><p>Findings on x-ray include soft tissue swelling, osteopenia, loss of joint space, erosions, growth disturbances (epiphyseal overgrowth) and joint subluxation.</p><p>Hepatosplenomegaly may be seen on abdominal radiographs, and pericardial or pleural effusions may be seen on chest radiographs.</p><h5>MRI</h5><p>MRI shows synovial hypertrophy, joint effusions as well as osseous and cartilaginous erosions. Active synovitis is characterized by enhancement on T1-weighted gadolinium contrast studies.</p>- +<p><strong>Juvenile idiopathic arthritis </strong>(<strong>JIA</strong>) (also known as <strong>juvenile rheumatoid arthritis</strong> or <strong>Still's disease</strong>) is the most common chronic arthritic disease of childhood, and has multiple subtypes.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>The estimated incidence is around 6-20 per 100000 per annum <sup>3</sup>.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Oligoarticular or polyarticular arthritis of a duration of six weeks or longer must be present to diagnose JIA.</p><p>Patients may present with an acute onset of symptoms or a more gradual onset. Symptoms are often worse in the morning, but typically persist to some extent throughout the day.</p><p>In patients with systemic onset, intermittent spiking fevers are typically noted, which help distinguish JIA from other diseases such as infection, other inflammatory diseases and malignancy. A light pink rash involving the trunk and/or extremities is also frequently observed in patients with systemic onset.</p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><p>Imaging shows a varied spectrum of involvement, based on the severity and duration of the disease.</p><h5>Plain film</h5><p>Findings on x-ray include soft tissue swelling, osteopenia, loss of joint space, erosions, growth disturbances (epiphyseal overgrowth) and joint subluxation.</p><p>Hepatosplenomegaly may be seen on abdominal radiographs, and pericardial or pleural effusions may be seen on chest radiographs.</p><h5>MRI</h5><p>MRI shows synovial hypertrophy, joint effusions as well as osseous and cartilaginous erosions. Active synovitis is characterized by enhancement on T1-weighted gadolinium contrast studies.</p>
References changed:
- 6. Doria A, Kiss M, Lotito A et al. Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Knee: Evaluation with Contrast-Enhanced Color Doppler Ultrasound. Pediatr Radiol. 2001;31(7):524-31. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1007/s002470100474">doi:10.1007/s002470100474</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11486809">Pubmed</a>
- 5. Sofka C & Bogner E. Imaging of Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis. HSS J. 2008;4(1):71-3. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-007-9065-0">doi:10.1007/s11420-007-9065-0</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18751866">Pubmed</a>
- 3. Gylys-Morin V, Graham T, Blebea J et al. Knee in Early Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis: MR Imaging Findings. Radiology. 2001;220(3):696-706. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2203000461">doi:10.1148/radiol.2203000461</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11526269">Pubmed</a>
- 4. Williams R & Ansell B. Radiological Findings in Seropositive Juvenile Chronic Arthritis (Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis) with Particular Reference to Progression. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985;44(10):685-93. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.44.10.685">doi:10.1136/ard.44.10.685</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4051591">Pubmed</a>
Image 1 X-ray (Frontal) ( create )
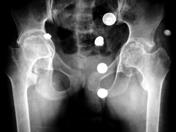
Image 3 X-ray (Frontal) ( create )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.