Kartagener syndrome
Updates to Article Attributes
Kartagener syndrome is a subset of primary ciliary dyskinesia, an autosomal recessive condition characterised by an abnormal ciliary structure or function, leading to impaired mucociliary clearance.
Epidemiology
The prevalence of primary ciliary dyskinesia is approximately 1 in 12,000-60,000 5. Approximately 50% of patient with primary ciliary dyskinesia have Kartagener syndrome/situs abnormality. No gender predilection is recognised.
Clinical presentation
Kartagener syndrome is characterised by the clinical triad of 1:
Other features include:
- telecanthus: widened interpupillary distance by a nasal polyp
- infertility in males
- subfertility in females
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
Chest radiographic findings depend on the severity of underlying bronchiectasis. Findings may include bronchial wall thickening, bronchial dilatation with the loss of normal peripheral tapering:
- predilection to involve the right middle, lingular segment of the left upper lobe and the lower lobes
- mucus plugs may be visible, finger in glove sign
- consolidation
- situs abnormality, i.e. situs inversus
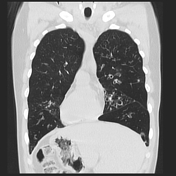
CT
CT tends to demonstrate bronchiectasis which may be variable in severity. However, changes are much milder than in cystic fibrosis 4. The morphology of bronchiectasis can be tubular/cylindrical or saccular/cystic. Also, CT demonstrates:
- consolidation
- mucocoele, impacted mucus in bronchioles
- tree-in-bud pattern or centrilobular nodules may be encountered with mucus impaction and endobronchial spread of infection
- mosaic perfusion/air trapping as ancillary findings
- eventual scarring may result from recurrent infection, requiring pulmonary resection surgery
Differential diagnosis
Situs abnormality with associated lower lobe bronchiectasis should prompt the diagnosis of Kartagener syndrome. However, there is a differential:
- hereditary impaired mucociliary clearance
- impaired immunity
- hypersensitivity and immune reaction
History and etymology
Manes Kartagener was a Zurich pulmonologist who first reported the clinical triad of sinusitis, bronchiectasis, and situs inversus in 1933 3. It was not until the 1970s, Bjorn Afzelius, an ultrastructuralist, noted the associated infertility in males. Afzelius noted the diversity of structural defects which can affect the dynein arms and/or radial spokes of the sperm tail 3.Further work was undertaken by Jennifer Sturgess, an ultrastructuralist from Toronto who identified the radial spoke defect as a common feature of Kartageners syndrome and immotile cilia syndrome. She also contributed to research in cystic fibrosis which shares clinical similarity to primary ciliary dyskinesia.
See also
-</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>Plain radiograph</h5><p>Chest radiographic findings depend on the severity of underlying <a title="Bronchiectasis" href="/articles/bronchiectasis">bronchiectasis</a>. Findings may include bronchial wall thickening, bronchial dilatation with the loss of normal peripheral tapering:</p><ul>- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>Plain radiograph</h5><p>Chest radiographic findings depend on the severity of underlying <a href="/articles/bronchiectasis">bronchiectasis</a>. Findings may include bronchial wall thickening, bronchial dilatation with the loss of normal peripheral tapering:</p><ul>
-<li>mosaic perfusion/<a title="Air trapping" href="/articles/air-trapping">air</a><a href="/articles/air-trapping"> trapping</a> as ancillary findings</li>- +<li>mosaic perfusion/<a href="/articles/air-trapping">air</a><a href="/articles/air-trapping"> trapping</a> as ancillary findings</li>
Image 6 CT (lung window) ( create )