Quadrigeminal plate
Updates to Article Attributes
Body
was changed:
The quadrigeminal plate, also known as the tectal plate or tectum, is constituted by the superior and inferior colliculi.
The tectum is the dorsal portion of the midbrain (brainstem), located posteriorly to the mesencephalic aqueduct. It derives from the alar plate of the neural tube during embryonic development.
Masses in the region of the tectum can obstruct the cerebral aqueduct resulting in obstructive hydrocephalus.
History and etymology
Derives from the Latin word "tectum" meaning "roof".
Vascularization
Vascularization is providedSupplied by the collicular (or quadrigeminal) artery. It is, a branch of the P1 (sometimes P2) segment of the posterior cerebral artery.
Related pathology
-<p>The <strong>quadrigeminal plate</strong>, also known as the <strong>tectal plate</strong> or <strong>tectum,</strong> is constituted by the <a href="/articles/superior-colliculi">superior</a> and <a href="/articles/inferior-colliculi">inferior colliculi</a>.</p><p>The tectum is the dorsal portion of the midbrain (<a href="/articles/brainstem">brainstem</a>), located posteriorly to the <a href="/articles/cerebral-aqueduct-of-sylvius">mesencephalic aqueduct</a>. It derives from the alar plate of the <a href="/articles/neural-tube">neural tube</a> during embryonic development.</p><p>Masses in the region of the tectum can obstruct the <a href="/articles/cerebral-aqueduct-of-sylvius">cerebral aqueduct</a> resulting in <a href="/articles/obstructive-hydrocephalus">obstructive hydrocephalus</a>.</p><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>Derives from the Latin word "tectum" meaning "roof".</p><h4>Vascularization</h4><p>Vascularization is provided by the collicular (or quadrigeminal) artery. It is a branch of the P1 (sometimes P2) segment of <a href="/articles/posterior-cerebral-artery">PCA</a>.</p><h4>Related pathology</h4><ul>- +<p>The <strong>quadrigeminal plate</strong>, also known as the <strong>tectal plate</strong> or <strong>tectum,</strong> is constituted by the <a href="/articles/superior-colliculi">superior</a> and <a href="/articles/inferior-colliculi">inferior colliculi</a>.</p><p>The tectum is the dorsal portion of the midbrain (<a href="/articles/brainstem">brainstem</a>), located posteriorly to the <a href="/articles/cerebral-aqueduct-of-sylvius">mesencephalic aqueduct</a>. It derives from the alar plate of the <a href="/articles/neural-tube">neural tube</a> during embryonic development.</p><p>Masses in the region of the tectum can obstruct the <a href="/articles/cerebral-aqueduct-of-sylvius">cerebral aqueduct</a> resulting in <a href="/articles/obstructive-hydrocephalus">obstructive hydrocephalus</a>.</p><h4>History and etymology</h4><p>Derives from the Latin word "tectum" meaning "roof".</p><h4>Vascularization</h4><p>Supplied by the collicular (or quadrigeminal) artery, a branch of the P1 (sometimes P2) segment of the <a title="Posterior cerebral artery" href="/articles/posterior-cerebral-artery">posterior cerebral artery</a>.</p><h4>Related pathology</h4><ul>
Images Changes:
Image ( update )
Position
was set to
.
Image 2 Diagram ( update )

Position
was set to
.
Image 3 Diagram ( update )

Position
was set to
.
Image 4 Pathology (Gross pathology) ( update )

Position
was set to
.
Image 5 Annotated image (Sagittal non-contrast) ( create )
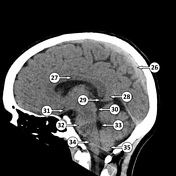
Image 6 Annotated image (Axial non-contrast) ( create )

Image 7 Diagram ( update )

Position
was set to
.