Transsphenoidal basilar skull fracture
Updates to Article Attributes
Body
was changed:
Transsphenoidal basilar skull fractures are a particularly serious type of basilar skull fracture usually occurring in the setting of severe traumatic brain injury and with potential for serious complications including damaging the internal carotid arteries and optic nerves as well as high incidence of dural tear with CSF leak.
Pathophysiology
Due to the particulars of the anatomy of the base of skull, fractures that involve the sphenoid sinus tend to extend along a number of predefined pathways 1,2:
- anterior transverse
- impact: lateral in the region of the temple
-
coronal fracture plane
- extending from the squamous temporal bone
- through the base of the anterior clinoid processes anterior to the pituitary fossa
- continuing laterally along the contralateral sphenotemporal buttress +/- into squamous temporal bone
- may extend inferiorly to involve the pterygoid processes
- lateral frontal diagonal
- impact: lateral frontal/anterior malar eminence
-
oblique fracture plane
- extending from lateral frontal/lateral orbital roof
- through the sphenoid sinus
- though or adjacent to the contralateral carotid canal into sphenopetrosal synchondrosis
- extends as a petrous temporal bone fracture
- often associated with maxillary sinus fractures and lateral orbital wall
- posterior transverse
- impact: lateral, just anterior to the external acoustic meatus
- U-shaped fracture comprised of bilateral longitudinal temporal bone fractures (or mixed) united in the midline by a fracture through the posterior wall of sphenoid/clivus
- involves sphenopetrosal synchondrosis, foramen lacerum and carotid canal
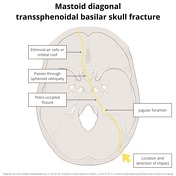
- mastoid diagonal
- impact: posterolateral in the mastoid region
-
oblique fracture
- originating in the occipital bone
- extending to the jugular foramen and petro-occipital fissure
- diagonally passing through sphenoid
- into contralateral ethmoid air cells or orbital roof
Content pending
-<li>anterior transverse<ul><li> </li></ul>- +<li>anterior transverse<ul>
- +<li>impact: lateral in the region of the temple</li>
- +<li>coronal fracture plane<ul>
- +<li>extending from the squamous temporal bone</li>
- +<li>through the base of the anterior clinoid processes anterior to the pituitary fossa</li>
- +<li>continuing laterally along the contralateral sphenotemporal buttress +/- into squamous temporal bone</li>
- +</ul>
-<li>lateral frontal diagonal</li>-<li>posterior transverse</li>-<li>mastoid diagonal</li>-</ul><p><em><strong>Content pending</strong></em></p>- +<li>may extend inferiorly to involve the pterygoid processes</li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>lateral frontal diagonal<ul>
- +<li>impact: lateral frontal/anterior malar eminence</li>
- +<li>oblique fracture plane<ul>
- +<li>extending from lateral frontal/lateral orbital roof</li>
- +<li>through the sphenoid sinus</li>
- +<li>though or adjacent to the contralateral carotid canal into <a href="/articles/sphenopetrosal-synchondrosis">sphenopetrosal synchondrosis</a>
- +</li>
- +<li>extends as a <a href="/articles/temporal-bone-fractures-1">petrous temporal bone fracture</a>
- +</li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>often associated with maxillary sinus fractures and lateral orbital wall</li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>posterior transverse<ul>
- +<li>impact: lateral, just anterior to the <a href="/articles/external-auditory-canal">external acoustic meatus</a>
- +</li>
- +<li>U-shaped fracture comprised of bilateral <a href="/articles/longitudinal-temporal-bone-fractures-1">longitudinal temporal bone fractures</a> (or mixed) united in the midline by a fracture through the posterior wall of sphenoid/clivus</li>
- +<li>involves <a href="/articles/sphenopetrosal-synchondrosis">sphenopetrosal synchondrosis</a>, foramen lacerum and carotid canal</li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>mastoid diagonal<ul>
- +<li>impact: posterolateral in the mastoid region</li>
- +<li>oblique fracture <ul>
- +<li>originating in the <a href="/articles/occipital-bone">occipital bone</a>
- +</li>
- +<li>extending to the <a href="/articles/jugular-foramen-2">jugular foramen</a> and <a href="/articles/petro-occipital-synchondrosis-1">petro-occipital fissure</a>
- +</li>
- +<li>diagonally passing through sphenoid</li>
- +<li>into contralateral <a href="/articles/ethmoidal-air-cells">ethmoid air cells</a> or orbital roof </li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +</ul>
References changed:
- 1. Venous Sinus Thrombosis in Blunt Trauma: Incidence and Risk Factors Slasky, Shira E. MD*; Rivaud, Yayone MD*; Suberlak, Matthew MD*; Tairu, Oluwole MD*; Fox, Adam D. MD†; Ohman-Strickland, Pamela PhD‡; Bilinisky, Esther MD, MS* Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography: November/December 2017 - Volume 41 - Issue 6 - p 891–897 doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000620 Neuroradiology
- 1. West OC, Mirvis SE, Shanmuganathan K. Transsphenoid basilar skull fracture: CT patterns. Radiology. 188 (2): 329-38. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.188.2.8327674">doi:10.1148/radiology.188.2.8327674</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8327674">Pubmed</a> <span class="ref_v4"></sp
Images Changes:
Image ( create )
Image 1 Diagram (Lateral frontal diagonal) ( create )

Image 3 Diagram (Posterior transverse) ( create )

Position
was set to
.
Image 4 CT (bone window) ( create )
Image 5 Diagram (Mastoid diagonal) ( create )
Position
was set to
.
Image 7 Diagram (Anterior transverse) ( create )

Position
was set to
.







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.