Presentation
Sudden onset of severe headaches.
Patient Data


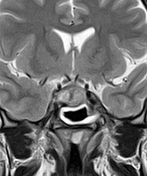

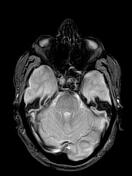

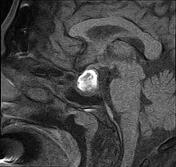

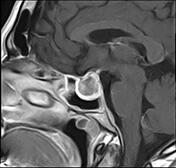

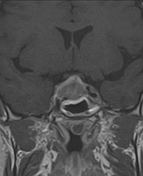

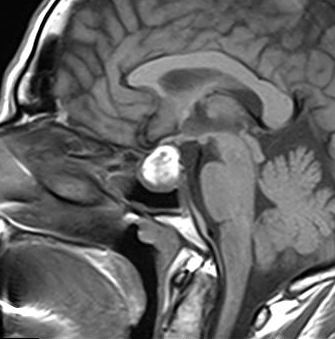
Sellar mass with suprasellar extension, elevating the optic chiasma. It displays a high signal centrally on T1 and T2 and a low signal on GE, not attenuated on T1 fat sat sequence (hemorrhagic infarct). The postcontrast sequences demonstrate peripheral enhancement.
Case Discussion
The clinical context and the MRI features in a patient known for pituitary macroadenoma are highly suggestive of pituitary apoplexy.
Pituitary apoplexy is an acute clinical condition caused by either hemorrhagic or non-hemorrhagic necrosis of the pituitary gland.
An existing pituitary macroadenoma is present in 60-90% but has been reported in healthy pituitary glands in a few isolated cases.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.