Presentation
Gradually developing swelling of abdominal wall followed by abdominal pain.
Patient Data
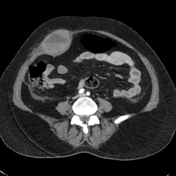

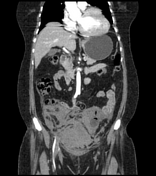

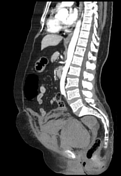

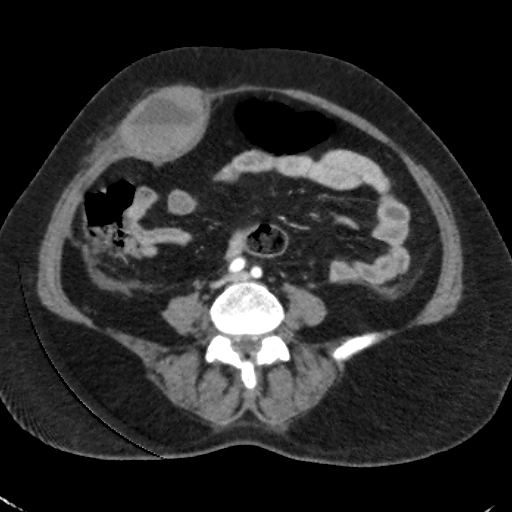
Right rectus muscle large haematoma is showing blood-fluid level and is extending into the right pelvic cavity. Evidence of active bleeding is seen.
The mass lesion exerts mass effects on adjacent organs, displacing the urinary bladder towards the left, encasing right external iliac vessels without significant luminal narrowing, closely abutting ipsilateral iliacus and obturator internus muscles and adjacent gut loops. Significant mesenteric fat stranding is seen.
The urinary bladder is empty with Foley's bulb in situ.
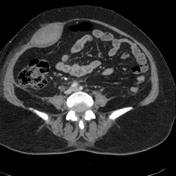

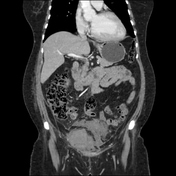

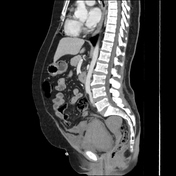

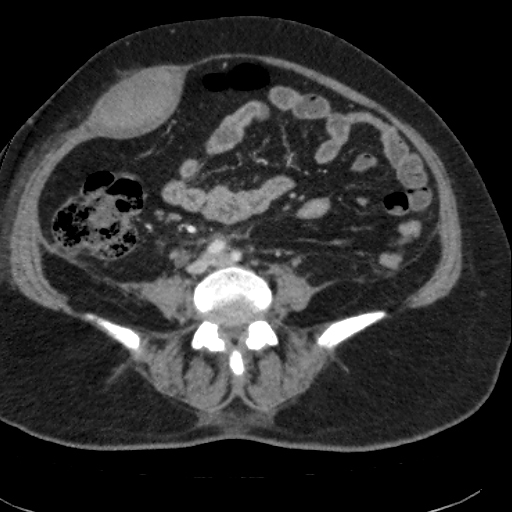
The patient was treated accordingly for a few days and had a repeat CT scan, which showed a significant decrease in the size of the haematoma.
The urinary bladder is empty with Foley's bulb in situ.
Case Discussion
CT findings in keeping with history of taking anticoagulant are more in favour of abdominal wall rectus sheath haematoma formation with associated pelvic cavity haematoma.
Repeat CT scan shows significant regression of the haematoma.
The patient is on anticoagulant therapy for ischaemic heart disease.
The main source of bleeding is from rupture of epigastric vessels.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.