Presentation
Left iliac fossa pain referred by urologist as suspected left ureteric stone.
Patient Data
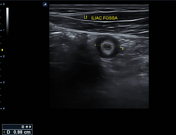
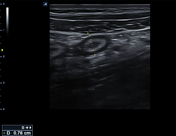

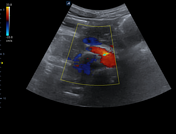
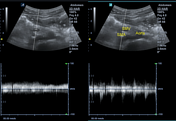
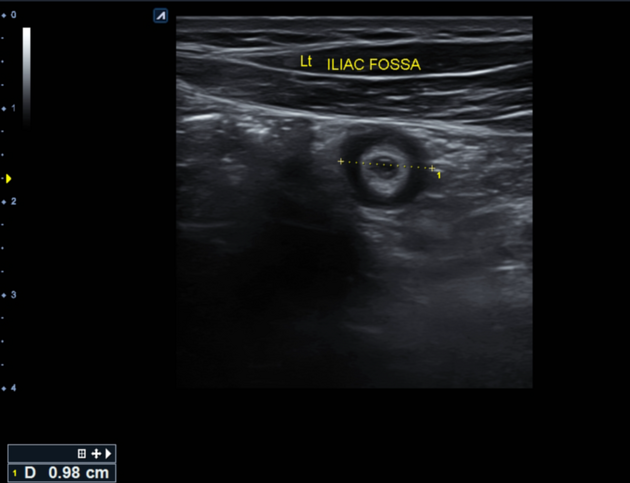
The left iliac fossa shows a tubular blind end structure measuring up to 9.8 mm with a target sign in cross-section. It's non-compressible and fluid-filled, surrounded by echogenic and thickened fat and regional reactive lymph nodes.
During the abdominal examination, normal liver and spleen positions were observed.
Signs of acute appendicitis were seen on the opposite side, at the left iliac fossa.
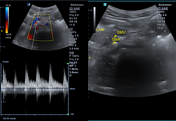
The position of the SMA and SMV revealed a reversed position, with the SMV seen ventral and to the left of the SMA, as confirmed by color Doppler and spectral wave.
Case Discussion
This case demonstrates findings of acute appendicitis on the opposite side, at the left iliac fossa, associated with intestinal nonrotation. The patient underwent surgical appendectomy from the left iliac fossa, and intestinal nonrotation was confirmed.
Intestinal non-rotation is a type of midgut malrotation in which the small bowel occupies the right side of the peritoneal cavity and the colon predominantly on the left. Patients with intestinal non-rotation have a lower incidence of midgut volvulus than other types of malrotation.
Other syndromes associated with reversed bowel position include situs inversus and heterotaxy syndrome.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.