Presentation
Fever, headache, and altered sensorium.
Patient Data
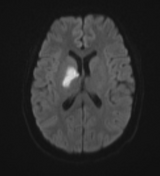

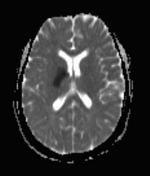

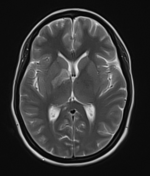

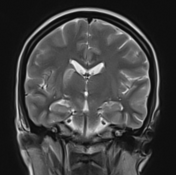

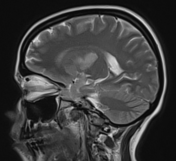

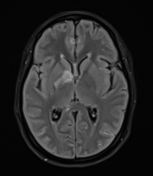

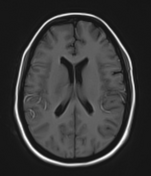

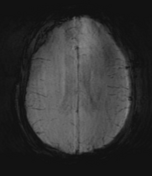


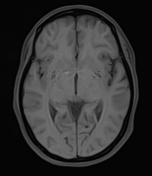

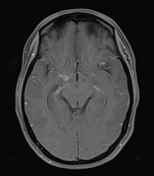

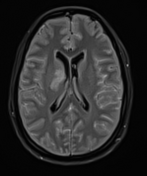

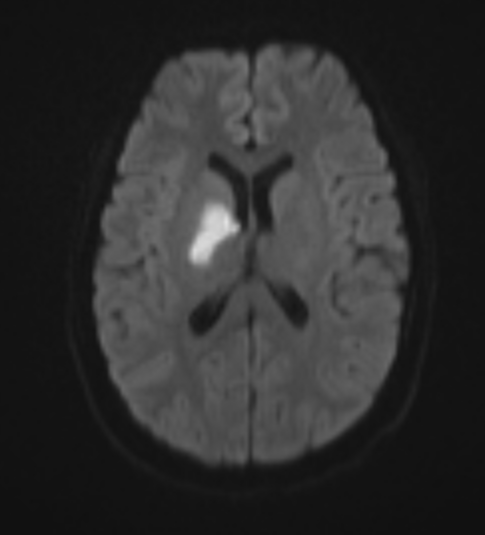
Moderate-sized area of diffusion restriction on DWI in the right basal ganglia involving the globus pallidus and internal capsule, superiorly extending up to the ipsilateral corona radiata region and inferiorly extending up to the medial temporal lobe with corresponding hyperintensity on T2W /FLAIR images. Mild diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement is seen along the cerebral hemisphere's cortical sulci, along the bilateral basal cistern (R> L), and interpeduncular cistern. The leptomeningeal enhancement is best seen on FLAIR post-contrast images.




The CSF study shows lymphocytic-predominant pleocytosis, elevated protein, and low glucose.
Case Discussion
The above imaging findings and CSF study are suggestive of an acute ischemic infarct with tuberculous meningitis.
The acute ischemic infarct in tuberculous meningitis is likely due to vasospasm or secondary to the vasculitis and is one of the known complications.
Co-author: Dr. Sanaullah Mudassir (DM, Neuromedicine).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.