Presentation
Bifrontal pulsatile headache with a pain scale rating of 8/10, left hemiparesis, labial commissure deviation, gait disturbance, nausea, and diaphoresis.
Patient Data
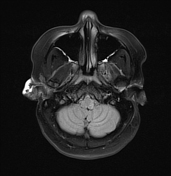

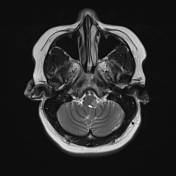



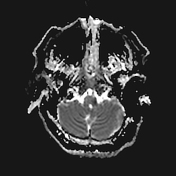

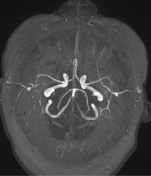
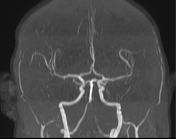
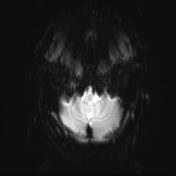

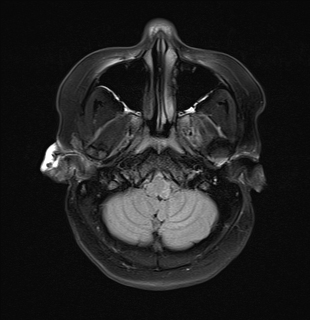
Inferior medullary infarct on the left side of the medulla, exhibiting T1 hypointensity and T2-FLAIR hyperintensity, along with restriction observed in DWI/ADC.
Case Discussion
The common signs include the triad of Horner with ipsilateral ataxia, contralateral hypoalgesia, and ipsilateral facial hypalgesia. In all of these patients, the diagnosis should be considered in individuals with sudden-onset symptoms and signs localising to the medulla.
DWI showed high sensitivity in the diagnosis of Wallenberg's lateral medullary syndrome, thus supporting the clinical findings at various stages and degrees of the disease. Wallenberg's syndrome is a brainstem infarction that presents as a distinct syndrome due to its location, size, and clinical symptoms.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.