Presentation
Sudden onset of chest pains and dyspnoea.
Patient Data


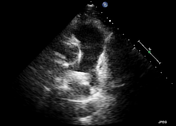

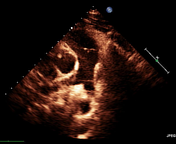

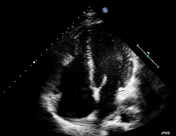

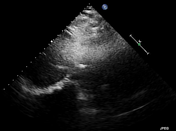

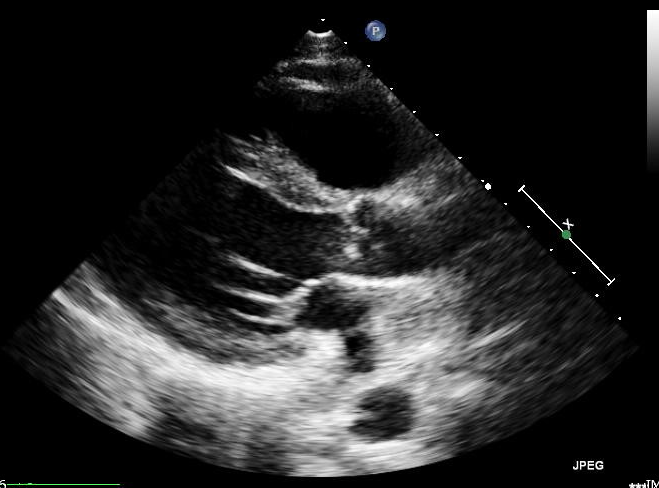
There is an echogenic lesion seen at the bifurcation of the main pulmonary artery partially obstructing the left pulmonary artery consistent with a thrombus. Dilated right cardiac chambers.
Moderate tricuspid regurgitation with severely elevated pulmonary pressures (not shown).
Good left ventricular systolic function.
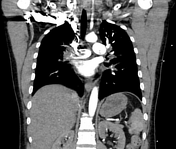

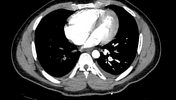

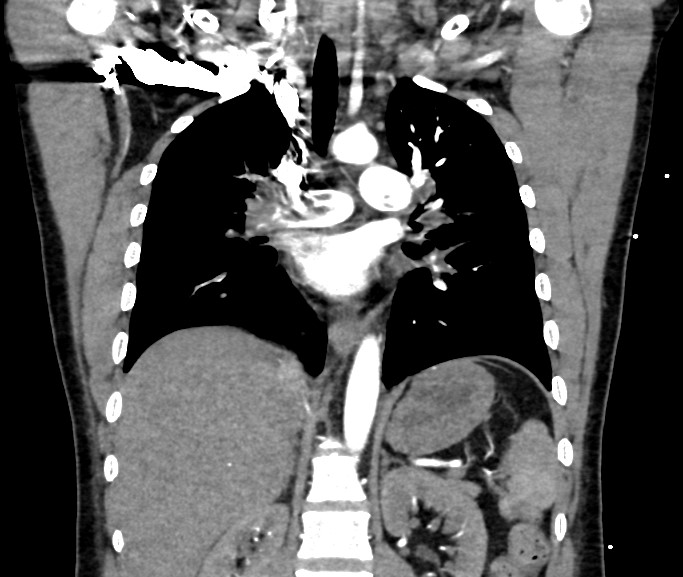
There are filling defects on right and left pulmonary arteries extending to its lobar and segmental branches due to thromboembolism (saddle thrombus).
Pulmonary trunk is patent and of normal calibre.
Both lungs exhibit normal attenuation and were well applied to the chest walls. No pleural thickening or effusion is demonstrated. Cardiac configuration and size are normal. No mediastinal mass or adenopathy is demonstrated. Tracheobronchial tree is normal. Chest wall and dorsal spine are unremarkable.
Case Discussion
D-dimer: 2906 ng/mL (Normal range 0-500 ng/mL).
This is a case of acute pulmonary embolism. Acute pulmonary embolism is a common and often fatal complication of venous thromboembolic disease.
Imaging plays an important role in the evaluation and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is the current gold standard of imaging and provides accurate diagnosis.
Patient was put on anticoagulation therapy.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.