Presentation
Acute right lower quadrant pain.
Patient Data


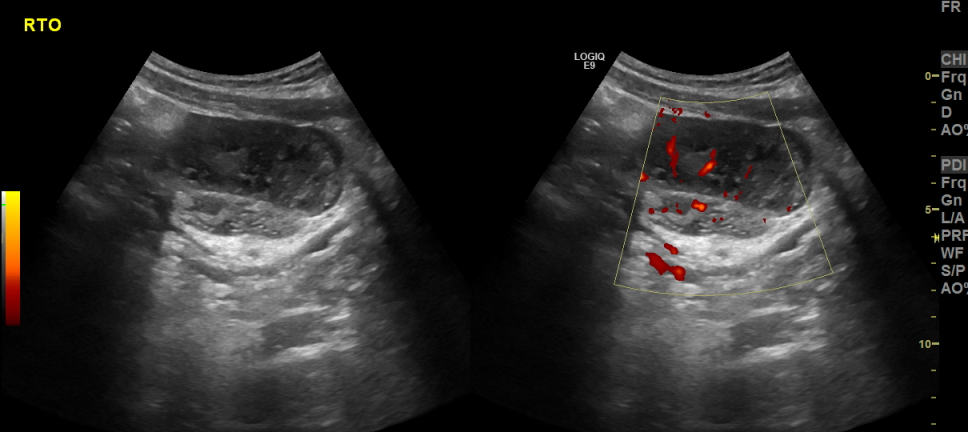
The right ovary appears significantly enlarged (measuring around 65 mL) in volume and edematous in comparison to the left ovary which is barely visualized.
Mild amount of pelvic free fluid is noted.
The vascularity was preserved.
Features are likely suggestive of early right adnexal torsion.
Case Discussion
Ovarian torsion is a relatively common gynecological emergency that requires early detection to preserve ovarian function.
Earlier in adnexal torsion, the gonadal vein is compressed within the pedicle, and failure of blood drainage results in tissue edema, that's why a significant volume difference is an alarming sign for early adnexal torsion.
Abnormal ovarian blood flow parameters and the presence of pelvic free fluid were the most diagnostically reliable isolated sonographic signs for ovarian torsion in multiple studies.
Another subtle sign of early ovarian torsion is the follicular ring sign seen around one or two follicles in this patient.
In our case, the vascularity appeared normal, and on laparoscopic evaluation, the right adnexa was twisted three full turns around the pedicle.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.