Alveolar hemorrhage and possible lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis in systemic lupus erythematosus
Updates to Case Attributes
The patient deteriorated; the haemoptysis became massive and the patient died shortly after ICU admission. A post-mortem was carried out and confirmed massive alveolar haemorrhage, a recognised complication of systemic lupus erythematosus.
The central lung cysts are suggestive of lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis, of which SLE is one of the associations.
Updates to Study Attributes
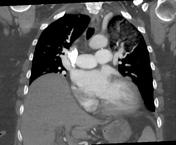
Numerous intrapulmonary cysts, the largest measuring 3 cm in the left lowerlobe.Left Left upper lobe ground glass opacity occupies most of the apical segment.Regional Regional cysts demonstrate air-fluid levels.Several Several pulmonary nodules:17 17 x 14mm right lower lobe anterior segment (image 23 se 6); this nodule isof fluid attenuation7 x 7mm right upper lobe (image 14 se 6)6 6 x 6mm right apex (image 9 se 6)7 7 x 6mm right lower lobe anterior basal segment (image 25 se 6)No No thoracic lymphadenopathy.Moderately Moderately severe cardiomegaly.
Dense pleural calcification, right medial basal region.Mild Mild central pulmonary arterial dilation.2 2 low attenuation hepatic lesions:14mm 14mm segment 2 anterior subcapsular (image 46 se 4) , 8mm segment 7 posterior subcapsular (image 43 se 4)
CONCLUSION:
Appearances suggest lymphoid interstitial pneumonia. The left upper lobe GGOhas a relatively wide DDx including haemorrhage and less likely aspirationor infection. Malignancy is considered unlikely.
Pulmonary hypertension.
No CT evidence of arterial dissection or pulmonary embolus.
Image CT (C+ CTPA) ( update )

Image CT (C+ CTPA) ( update )




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.