Presentation
Episode of syncope, after which the patient complained of right upper extremity weakness and facial paresthesia on the right. Incidental finding.
Patient Data
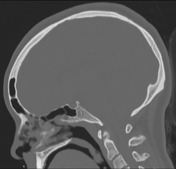

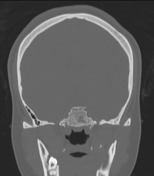

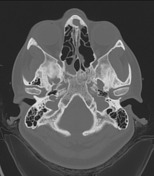

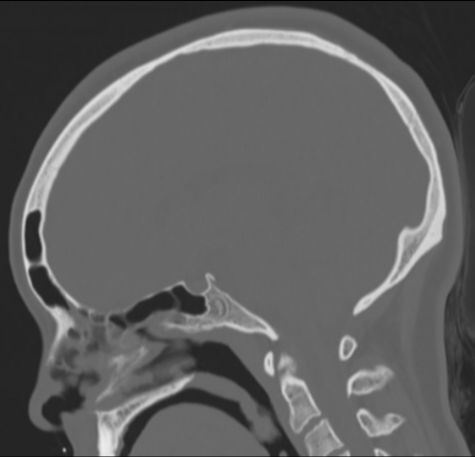
The sphenoid sinus shows arrested pneumatization, with soft tissue inclusions exhibiting thin bony walls. Cluster of small intraosseous spaces involving the clivus and sphenoid bone on the right, mimicking ectopic arachnoid granulation, one of which contains fat. Marked bilateral enlargement of posterior ethmoid air cells, probably compensatory.
Mucosal thickening around the left frontal ostium. Foamy content in the superior part of the right maxillary sinus.
Well-developed bilateral mastoid air cells, continuing into the squamous part of the temporal bone the petrous apex, to a greater extent on the left.
Case Discussion
Arrested pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus is speculated to occur due to changes in regional blood flow during childhood 1. The appearance can mimic several types of lesions known to "dwell" in this area (e.g. clival chordoma) that can be ruled out by looking for the following characteristics 2,3: hypoplastic, sclerotic sphenoid sinus with internal curvilinear calcifications and thin sclerotic borders; fat content on MRI; bilateral preserved vidian canal; no expansion or invasion of surrounding structures.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.