Presentation
Work-up of a first episode of seizures. Previously healthy patient.
Patient Data
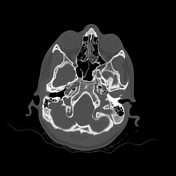

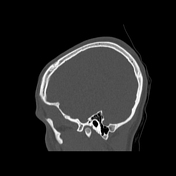

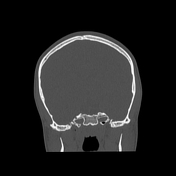

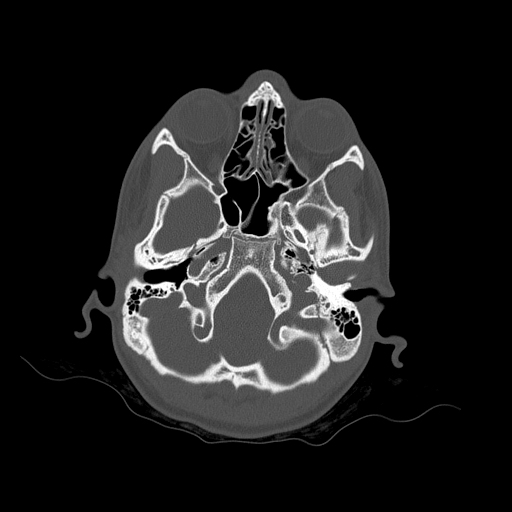
Bone reformation from non-contrast CT scan shows bilateral posterior condylar canal - note the position posteriorly to the occipital condyles.
No evidence of fractures, bone lesions or soft-tissue swelling.
Case Discussion
Incidental finding of bilateral posterior condylar canal, which is located posteriorly to the occipital condyle and lies in the condylar fossa. This variant is most often bilateral and contains emissary veins connecting extracranial and intracranial venous drainage from the head to the neck. Mentioning this and other anatomical variants regarding arterial or venous circulation may, at times, be of utmost importance for treatment planning, e.g. for treating craniocervical dural arteriovenous fistulas or malformations.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.