Presentation
Bilateral elbows pain. No history of trauma. Background of coeliac disease.
Patient Data
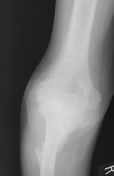

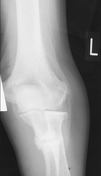
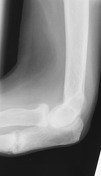
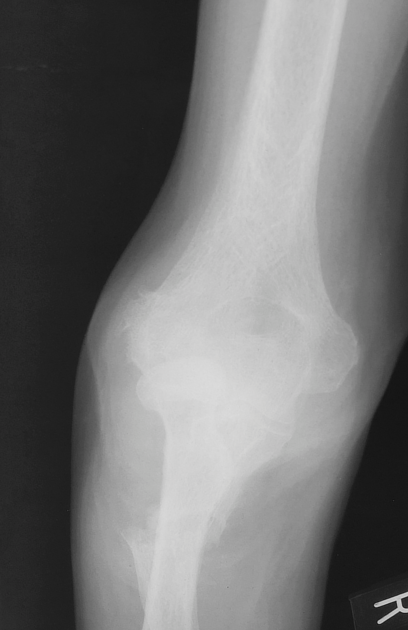
Plain radiographs of both elbow joints demonstrate a slightly superiorly displaced fracture of the right proximal ulnar shaft and a nondisplaced fracture of the left proximal ulnar shaft with cortical sclerosis of the osseous ends.
The fractures are symmetrical and perpendicular to the long axis of both ulnar bones and represent advanced pseudofractures - Looser zones.
Bilateral elbow joint effusions are also seen, more marked on the right.
Case Discussion
The case presents advanced pseudofractures (Looser zones) involving the proximal ulnar bones resulting from osteomalacia secondary to coeliac disease 1,2.
The proximal ulnae are a rare site of Looser zones, which are most commonly seen in the scapulae, femora or pubic rami.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.