Presentation
Infant with conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia.
Patient Data
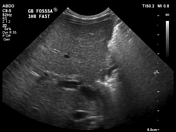

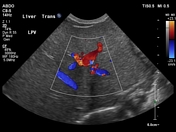

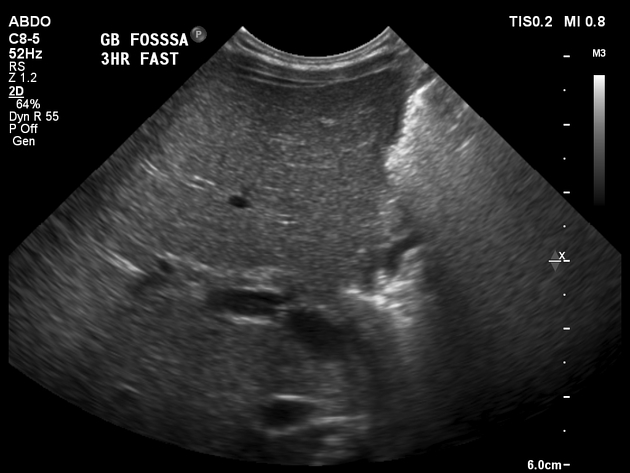
There is no identifiable gallbladder despite three hours of fasting. The extrahepatic common bile duct is not clearly identified.
The liver has a normal echogenicity and echotexture. Normal antegrade portal vein flow.


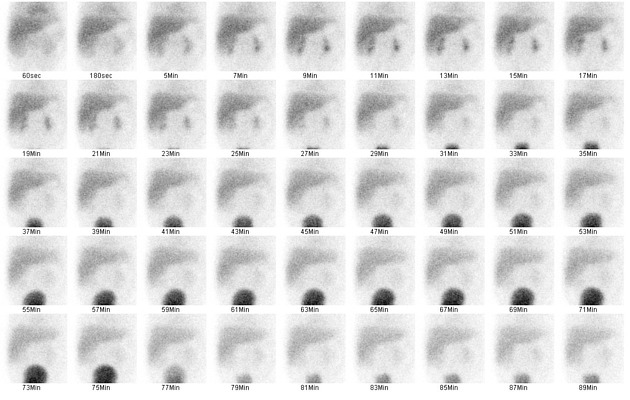
There is symmetrical extraction of radiotracer from the blood pool by both lobes liver. There is accumulation of radiolabelled radiotracer within the liver with no evidence of radiolabelled bile within the intra or extrahepatic biliary tree.
Delayed planar images do not demonstrate any evidence of radiolabelled bile within the small intestine.
Case Discussion
Biliary atresia is congenital disorder characterised by the absence or paucity of the extrahepatic biliary tree.
On ultrasound, the triangular cord sign refers to echogenic fibrous tissue adjacent to the portal vein, representing the abnormal bile duct. The gallbladder is absent in half of cases.
Early surgical intervention with Kasai procedure reduces the need for transplantation. Biliary atresia is the most common indication for liver transplantation in children.
This child developed cirrhosis despite Kasai procedure and required a liver transplant at age 1.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.