Presentation
Spastic hypotonic child with delayed milestones.
Patient Data


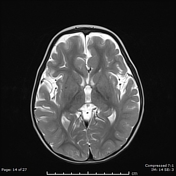

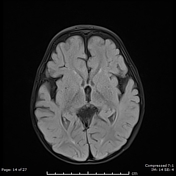


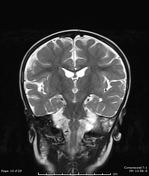

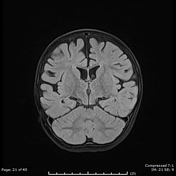

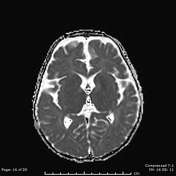

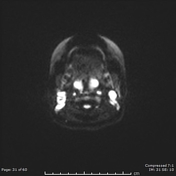

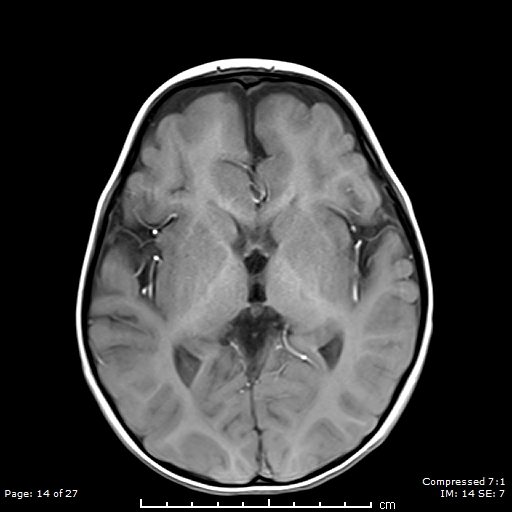
There are bilateral symmetrical T2 hyperintensities, with diffusion restriction of the central tegmental tracts, consistent with central tegmental tract T2 hyperintensity
Mild atrophic changes of bilateral cerebral hemispheres, mainly the bilateral frontal lobes.
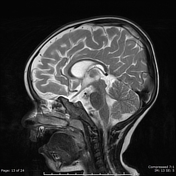
Diffuse thinning of the corpus callosum.
Incidental findings of retained fluid filling the left middle ear and left mastoid air cells.
Case Discussion
One of the earliest parts of brain myelination is called central tegmental tract, which is an extrapyramidal tract between the red nucleus (superiorly) and the inferior olivary nucleus (inferiorly).
These tracts are seen as T2/FLAIR/DWI high signal intensity, and can be seen in multiple conditions; most importantly in epilepsy and antiepileptic drugs (vigabatrin), but also can be seen in hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy, cerebral palsy, metabolic disorders and others 1.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.