Presentation
A 40-year-old male undergoes a thyroid uptake and scan for subclinical hyperthyroidism detected by a suppressed TSH.
Patient Data





Thyroid uptake and scan performed using 300 uCi of I-123 PO with images obtained 24-hours after administration.
24-hour uptake was 31%.
Anterior view shows an area of relative decreased radiotracer in the lower pole, left lobe, representing a cold nodule (red dashed circle).
No additional findings are seen on the LAO and RAO views.
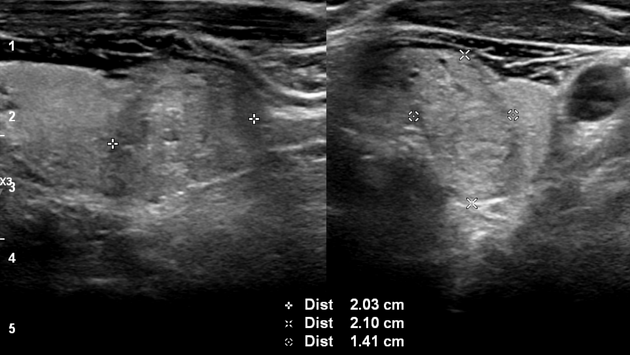
Ultrasound of the thyroid revealed a 2.1 cm nodule in the lower pole, left thyroid lobe corresponding with the cold nodule on prior thyroid scintigraphy. Nodule was solid, iso-echoic and taller-than-wide; consistent with ACR TI-RADS 4, moderately suspicious and warranting biopsy.
Biopsy of the left thyroid lobe nodule revealed a benign adenoma.
Case Discussion
A cold nodule on thyroid scintigraphy is indicative of a lesion with decreased or absent function in regards to the uptake and trapping of iodine. It carries an estimated 10-20% risk of malignancy and hence is typically further assessed by thyroid ultrasound. If the US does not show clearly benign features (such as an anechoic colloid cyst) tissue sampling is often pursued (as in this case)
Once acronym for the differential diagnosis of a cold nodule on thyroid scintigraphy is CATCH PALM and stands for:
Colloid cyst
Adenoma
Thyroiditis (focal)
Carcinoma
Haematoma
Parathyroid (hyperplastic)
Abscess
Lymphoma
Metastasis




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.