Complex regional pain syndrome
Updates to Case Attributes
Although there was no foot fracture, pain developed in the mid- and forefoot. Radiographs demonstrate severe regional osteopenia, typically in the periarticular regions, with appearances mimicking focal lytic bone lesions, typically in the periarticular regions.
-<p>Although there was no foot fracture, pain developed in the mid and forefoot. Radiographs demonstrate severe regional osteopenia with appearances mimicking focal lytic bone lesions, typically in the periarticular regions.</p>- +<p>Although there was no foot fracture, pain developed in the mid- and forefoot. Radiographs demonstrate severe regional osteopenia, typically in the periarticular regions, with appearances mimicking focal lytic bone lesions.</p>
Updates to Study Attributes
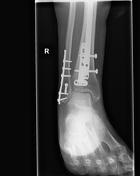
RIGHT LOWER LEG & ANKLE
Comparison is made with the previous examination from 28 August 2014several weeks earlier. Tibial intremedullaryintramedullary nail in unchanged position. There is delayed union of the oblique fracture through the distal tibial diaphysis. Screw and plate fixation of distal fibular fracture unchanged. There is non-union of the spiral proximal right fibular spiral fracture. The ankle joint alignment is normal. No new fracture identified.
Right foot
There is severe patchy osteopenia predominantly in periarticular distribution. No new fracture identified. The overall appearances are most in keeping with reflex sympathetic dystrophy (Sudeck atrophy).
Image X-ray (Mortise) ( update )
Updates to Study Attributes
Tibial intramedullary nail transfixes a comminuted tibial shaft fracture.
New posterior distal tibial plate and lateral malleolar plate and screws are noted.
Alignment at the mortise is within normal limits.
Minimally displaced proximal fibular fracture is unchanged in position.
Updates to Study Attributes
There has been no change in alignment of the intramedullary nail fixating a comminuted tibial diaphyseal fracture. Oblique fracture of the proximal fibular shaft is similar to previous.
Comminuted distal fibular fracture involving the lateral malleolus, displaced posterior tibial plafond fracture and minimally displaced medial malleolus fracturesfracture are similar to previous.