Presentation
Motor vehicle collision.
Patient Data
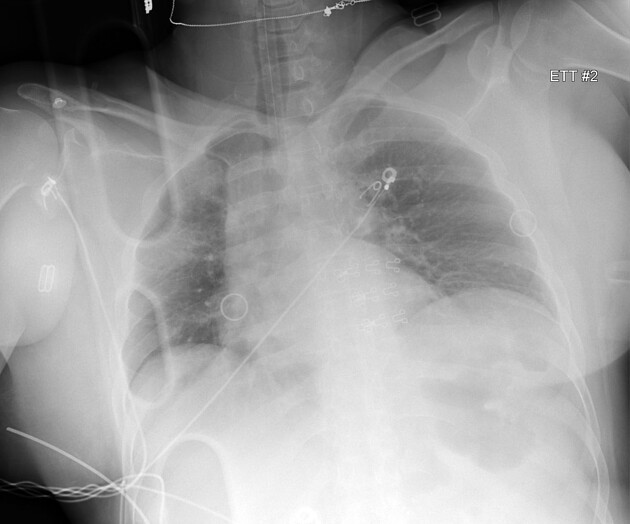
Endotracheal tube approporiately positioned. Lungs hypoinflated. Otherwise normal.
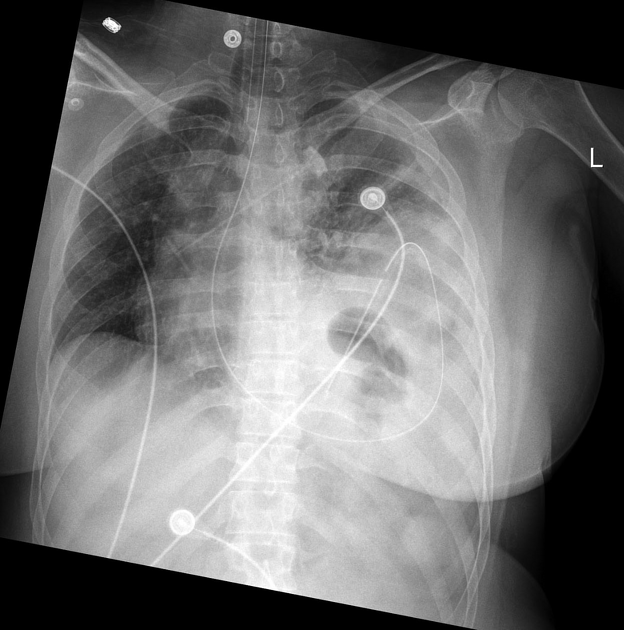
New nasogastric tube looped within a gas containing collection above the expected location of the left diaphragm. New left effusion, no pneumothorax.
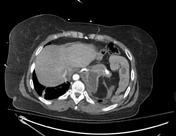

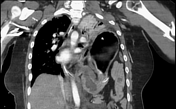

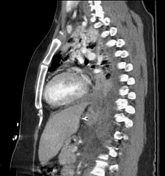

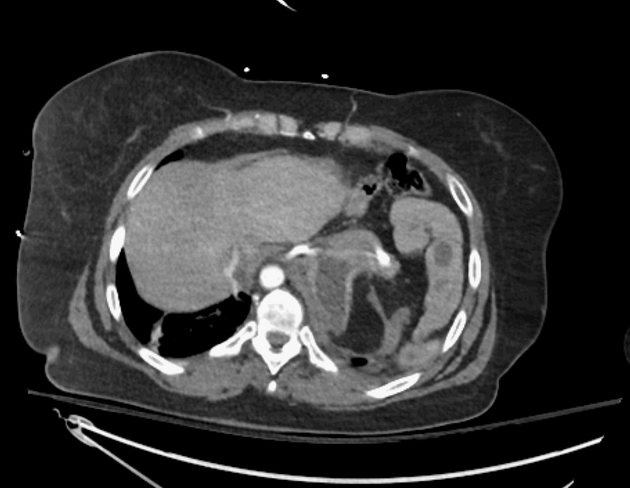
Left diaphragm rupture with intrathoracic herniation of stomach and bowel. Small left pleural effusion, atelectatic left lung.
Comminuted mid-shaft left humeral fracture.
Case Discussion
Apparent supradiaphragmatic course of a nasogastric tube in a trauma patient should raise suspicion for diaphragmatic rupture. Abdominal contents herniate through the diaphragmatic defect due to the pressure gradient from positive in the abdomen to negative in the pleural cavity. Traumatic left diaphragmatic hernia is much more frequent than the right: it is assumed that the liver protects the right diaphragm.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.