Presentation
Headache on the third day after a traffic accident. No focal neurological symptoms.
Patient Data
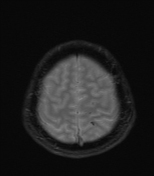

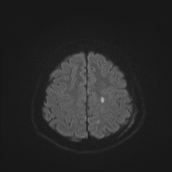

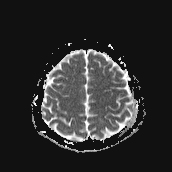

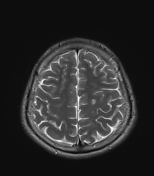

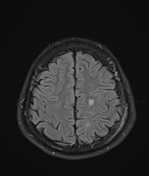

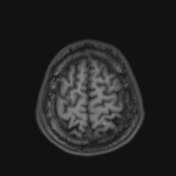

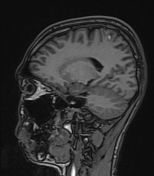

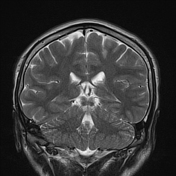

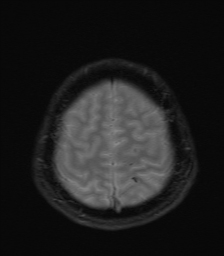
Several abnormal signal foci in the left frontoparietal lobe (brain parenchyma), the body of the corpus callosum, show high signal intensity on FLAIR and T2W, low signal on GRE, and restricted diffusion.
Soft tissue swelling of the scalp in the left parietal region.
Bone marrow oedema in the left parietal skull bone.
Case Discussion
The imaging findings in this case are consistent with stage 2 diffuse axonal injury.
Diffuse axonal injury often presents with severe clinical symptoms, including deep coma, while CT imaging may not reveal clear lesions. This makes diagnosis challenging.
MRI of the brain, especially with GRE or SWI sequences, has a higher sensitivity in detecting diffuse axonal injuries. This allows for the identification of microhaemorrhages or vascular lesions that CT may miss.
Differential diagnoses for this condition include:
micro haemorrhages in hypertensive encephalopathy
Accurate identification of these conditions is crucial for developing an appropriate treatment plan.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.