Presentation
History of left ear pinna piercing about 2 months back. It was followed by left external ear diffuse swelling.
Patient Data
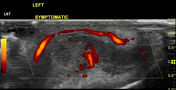


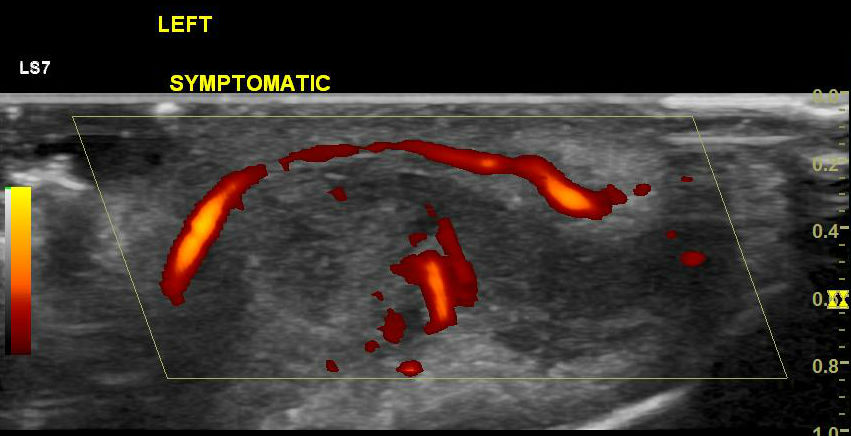
Affected left ear pinna shows thickening, the loss of normal well-defined margins with the presence of hypervascularity. It involves most of the helix and antihelix of the external ear cartilage. Tragus and antitragus are spared. The lobule is normal. There is a hypoechoic tiny tract from the skin to cartilage at the site of the piercing.
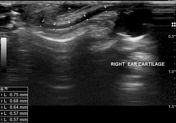
Asymptomatic right ear pinna shows normal thin cartilage with well-defined margins.
Case Discussion
The external ear pinna contains cartilage except in lobule. Ear piercing is more commonly done in the lobule and there is no risk of chondritis. When ear piercing is done in part of the pinna containing cartilage, there is a risk of chondritis as in this case. This patient had previous ear pinna piercing in lobule as well as in mid part of ear containing cartilage which was uneventful.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.