Presentation
Chronic nasal congestion, facial pain, and progressive proptosis with diplopia. There was no history of trauma or previous nasal surgery.
Patient Data


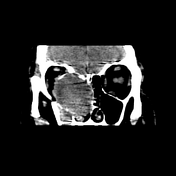

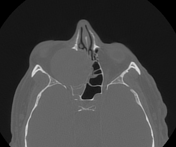

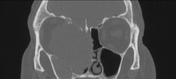

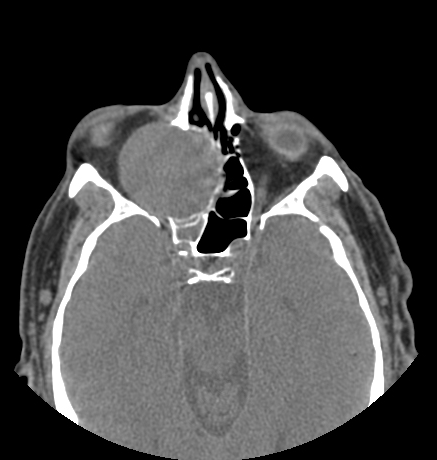
CT of paranasal sinuses showed a well-defined, rounded, and expansile lesion with a density similar to soft tissue centered at the right ethmoid cells. The lesion shows orbital extension by displacing the medial wall of the orbit laterally and its content, with subsequent proptosis.
Features are in keeping with ethmoid mucocele.
The lesion causes obstruction of the mucociliary drainage pathways (ostiomeatal unit, frontal recess and sphenoethmoidal recess) with opacification of right frontal, maxillary and sphenoid sinuses.
Case Discussion
An ethmoid mucocele is a benign, slow-growing, cystic lesion that develops within the ethmoid sinuses of the nasal cavity. It arises from the obstruction of the ethmoid sinus drainage pathway, leading to the accumulation of mucus and subsequent expansion of the sinus cavity. Blockage of the natural drainage pathways can occur due to various factors, such as chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, previous nasal trauma or surgery, or anatomical abnormalities that impede proper sinus drainage.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.