Presentation
Trauma. No seizure, weakness, or tremor. Normal neurological examination.
Patient Data
Age: 35 years
Gender: Male
From the case:
Fahr disease
Show annotations
Download
Info
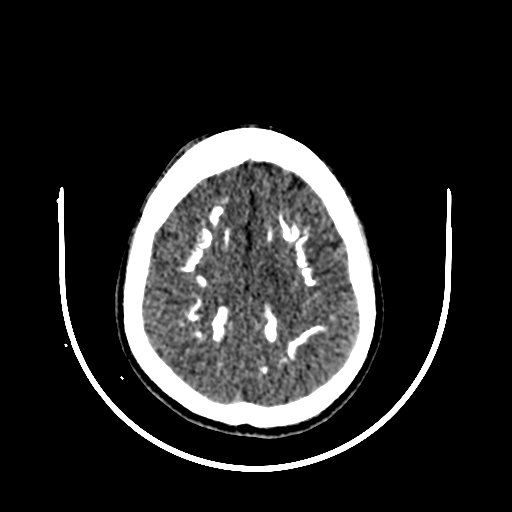
Diffuse symmetrical calcifications in the bilateral basal ganglia, thalami, midbrain (including red nuclei), pons, cerebellar hemispheres (including dentate nuclei), and subcortical white matter of the fronto-parieto-temporal lobes.
Case Discussion
Primary Fahr disease should only be considered when secondary causes of a Fahr syndrome are excluded, such as pseudohypoparathyroidism, mitochondrial diseases, infections (e.g. CMV, HIV), and radiation exposure.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.