
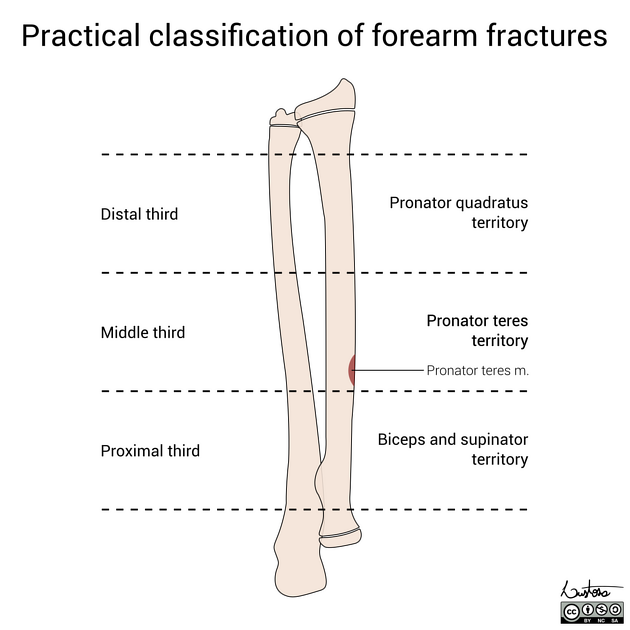
Illustrations of a practical classification of forearm fractures (2023 version).
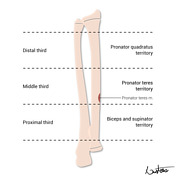
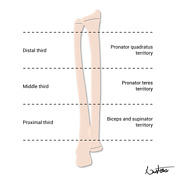
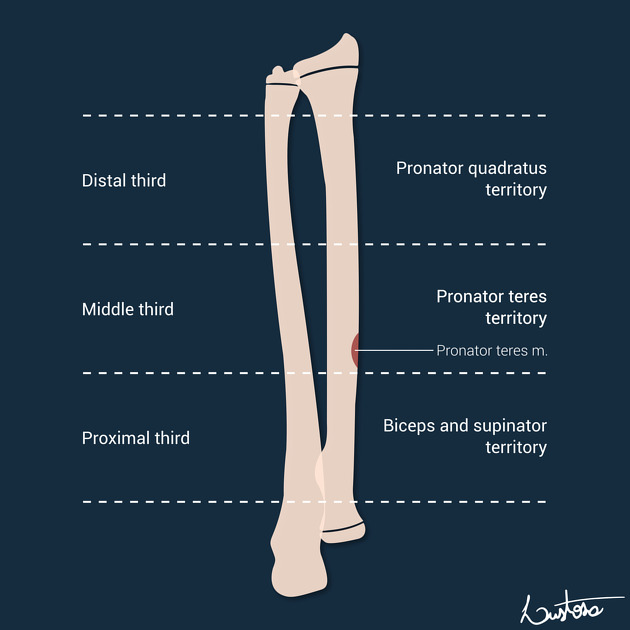
The pronator teres insertion is located on the proximal half of the middle third of the radial shaft.
(Download for better resolution)
Illustrations of a practical classification of forearm fractures.
The pronator teres insertion is located on the proximal half of the middle third of the radial shaft.
Case Discussion
Paediatric forearm fractures can be practically classified considering 3 main characteristics:
- bone involvement: radius, ulna, or both
- level: distal, middle, or proximal third
- fracture pattern: complete, greenstick, bowing, or comminuted
Unlike adults, most forearm fractures in children can be managed non-operatively.
The reduction manoeuvre and the position of immobilisation can be guided by this simple yet clinically practical classification.
If a middle third radial fracture is present, special attention is given to the pronator teres insertion, which dictates the immobilisation position. The pronator teres insertion is located on the proximal half of the middle third of the radial shaft.
For adults, the AO classification is more clinically relevant.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.