Presentation
A slowly growing mass in the neck.
Patient Data
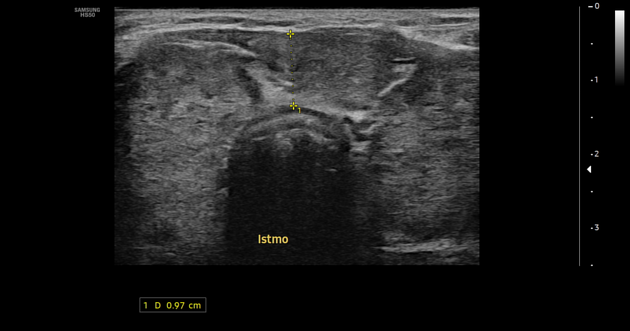
thyroid gland enlargement with a heterogeneous texture and lobulated contour on ultrasound
multiple hypoechoic micronodules scattered throughout, separated by echogenic septa
hypoechoic nodule in the posterior pole of the right thyroid lobe, potentially exhibiting both benign and malignant characteristics
increased Doppler signal, indicating increased vascularity in the area
Case Discussion
The case turned out to be Hashimoto thyroiditis, and the ultrasonographic characteristics of the lesions vary with the disease's state. In our case, the patient presented in an acute diffuse state, characterized by gland enlargement with lobulated margins and scattered hypoechoic nodules diffusely throughout the gland, along with increased Doppler signal 1.
Nodules in the presence of Hashimoto's thyroiditis typically appear as solitary, solid, non-calcified, and hyperechoic with a halo, while those without this condition may display cystic changes and eggshell calcifications 2.
It can be challenging to distinguish it from other diffuse thyroid parenchymal diseases such as Graves disease, De Quervain thyroiditis, or malignancies like thyroid lymphoma 2. Therefore, laboratory tests and clinical context always play a crucial role in the diagnosis.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.