Presentation
Chronic abdominal pain.
Patient Data
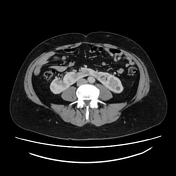






Horseshoe kidney with incidental small cysts but no calculi or hydronephrosis.
Abnormally positioned duodenojejunal flexure suggesting malrotation.
Incidental minor colonic diverticulosis.
Case Discussion
The patient's chronic abdominal pain was not explained by the findings.
Horseshoe kidneys are often asymptomatic and detected as an incidental finding on imaging. Complications of urinary stasis such as ureteric colic or urinary tract infection were absent in this case.
Embryological ascent and rotation of the kidneys are prevented by fusion of the lower poles; the isthmus cannot ascend past the inferior mesenteric artery.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.