Presentation
Prolonged cardiopulmonary resuscitation after a cardiac arrest during coronary intervention. Not waking up 24 hours after stopping sedation. Pupils are non-reactive to light.
Patient Data
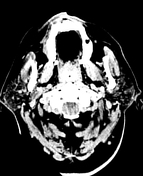

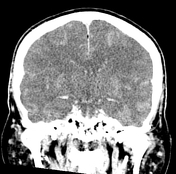

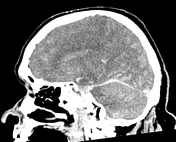

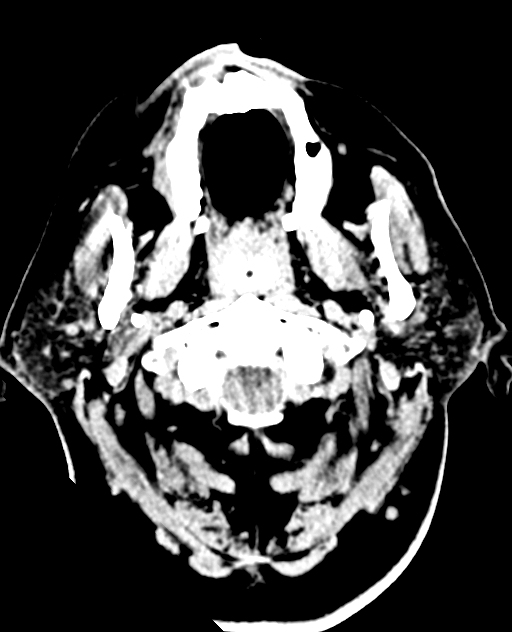
There is diffuse cerebral oedema with effacement of the sulcal spaces, ventricular compression and tonsillar herniation.
The normal attenuation of the grey and white matter is reversed (reversal sign) and the density of the cerebellum is relatively higher due to the hypoattenuation of the cerebral hemispheres (white cerebellum sign).
The basal cisterns demonstrate relatively increased attenuation due to cerebral oedema simulating subarachnoid haemorrhage. This is called pseudosubarachnoid haemorrhage.
Case Discussion
Hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy (adults and children) or global hypoxic-ischaemic injury is a common unfortunate consequence of prolonged resuscitation after cardiac arrest. The white cerebellum sign and reversal sign indicate irreversible brain injury and very poor prognosis.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.