Presentation
Chronic progressive dyspnoea , anaemia and recurrent haemoptysis.
Patient Data
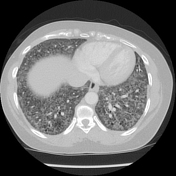





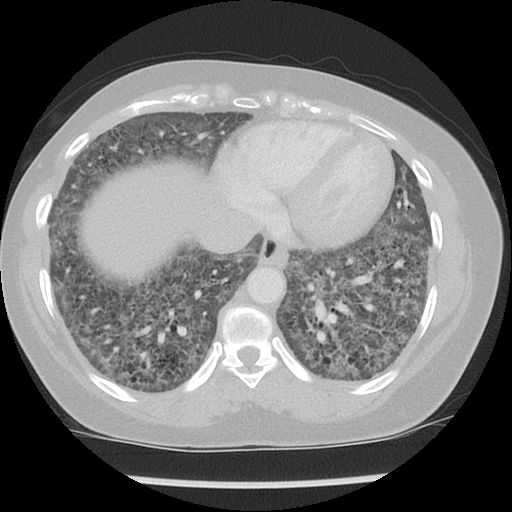
Widespread ground-glass lung opacity with centrilobular predominance.
Widespread macro- and micro-cystic appearance with relative sparing of the lung cortex.
Generalised mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
Normal heart chambers.
Multinodular thyroid.
Case Discussion
Bilateral sequential lung transplantation for irreversible respiratory failure due to idiopathic pulmonary haemosiderosis.
PATHOLOGY:
Microscopic Description:
Specimen 1: Right explanted native lung. Sections of lung parenchyma show marked diffuse interstitial fibrosis with usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)-like changes in a background of organising pneumonia with large Masson bodies rather than fibroblastic foci, prominent intra-alveolar haemorrhage, with numerous intra-alveolar haemosiderin laden macrophages within the alveolar lumina, as well as shedding and hyperplasia of the alveolar epithelial cells. There is marked alveolar capillary congestion. Aggregates of haemosiderin-laden macrophages are also identified within the pleura. There is no evidence of necrosis, no vasculitis, no granulomas and no lymphoid follicles identified. There are two benign lymph nodes identified within the specimen that show marked sinus histiocytosis with prominent aggregates of haemosiderin-laden macrophages.
Specimen 2: Left explanted lung. Sections of lung parenchyma show numerous haemosiderin-laden macrophages within the alveolar lumina, shedding and hyperplasia of the alveolar epithelial cells and marked alveolar capillary congestion. There is diffuse interstitial fibrosis with UIP-like changes but with more organising pneumonia and Masson bodies rather than fibroblastic foci and accompanying intra-alveolar haemorrhage. The changes within the left lung show less organising pneumonia and more features of interstitial fibrosis than within the right. Within both lungs, the changes are similar within the upper lobe and lower lobe with no lower lobe predominance. There is no overall subpleural or septal predominance. Within the left lobe haemosiderin appears to be aggregated more within the periphery and the pleura and in some areas the interstitial pneumonia changes are more akin to non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP-like) rather than heterogeneous appearances of UIP-like areas. There are two benign lymph nodes identified within the hilar region that show prominent sinus histiocytosis and aggregates of haemosiderin-laden macrophages.
Specimen 3: Subcarinal lymph node. Sections consist of two benign lymph nodes exhibiting marked sinus histiocytosis with prominent haemosiderin-laden macrophages aggregated within the node.
Specimen 4: Left hilar lymph node. There is a single lymph node identified which shows prominent sinus histiocytosis and marked aggregates of haemosiderin-laden macrophages.
COMMENT: The features identified within both lungs and lymph nodes are in keeping with interstitial fibrosis secondary to haemosiderosis. The differential diagnosis of primary idiopathic haemosiderosis includes disorders that produce secondary pulmonary alveolar bleeding and haemosiderosis such as mitral stenosis, periarteritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus (usually with neutrophils in alveolar septal capillaries) and systemic vasculitis. Please correlate carefully with clinical findings to exclude any secondary causes.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.