Presentation
Headache and loss of consciousness.
Patient Data


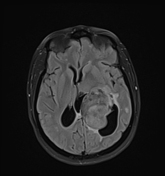

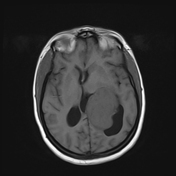

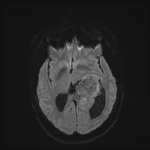

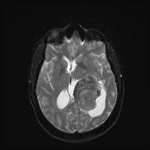

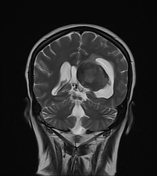

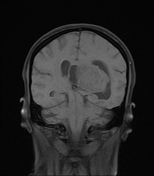

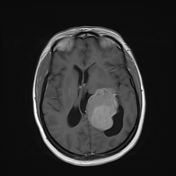

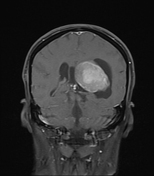

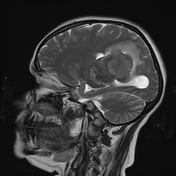

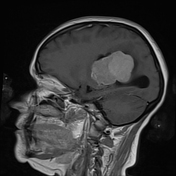

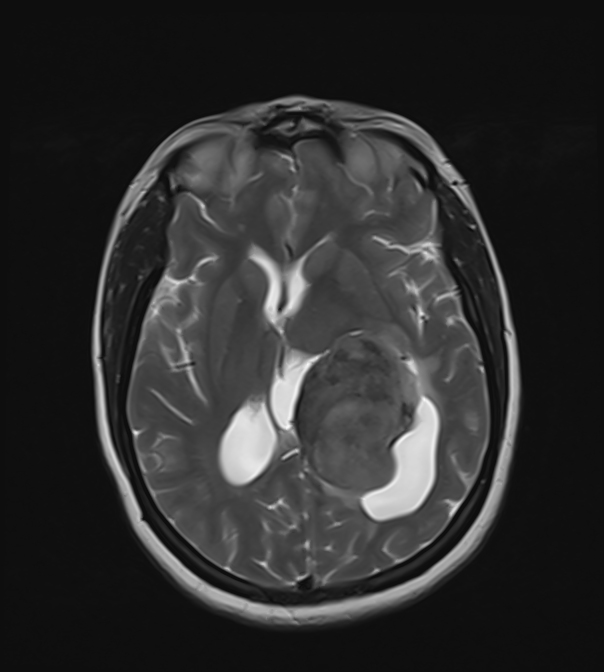
An intra-ventricular occupying lesion is centered at the atrium of the left lateral ventricle. It elicits isointense signals in T1 and heterogeneously hyperintense signals in both T2 and FLAIR images with avid post-contrast enhancement. The lesion is associated with dilatation of the ipsilateral lateral ventricle.
Bilateral frontoparietal subcortical foci of bright T2/FLAIR signal are noted, they are not surrounded by edema and exert no mass effect.
Case Discussion
intraventricular lesions include a variety of benign and malignant neoplasms
intraventricular meningiomas are usually seen in adults at the trigone of the lateral ventricle
choroid plexus tumors (papilloma and carcinoma) affect mainly the pediatric group, most commonly arising at the atria of the lateral ventricle, however, they can also arise from the 4th ventricle
central neurocytomas are seen in young adults, commonly in the lateral ventricles attached to the septum pellucidum
subependymomas are seen in middle-aged and older individuals and are commonly seen in the 4th ventricle
subependymal giant cell astrocytomas occur in young patients with tuberous sclerosis, near the foramen of Monro, they show calcifications, heterogeneous signal, and marked post-contrast enhancement




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.