Presentation
Acute right-sided weakness and aphasia.
Patient Data
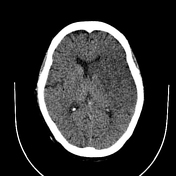

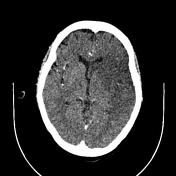

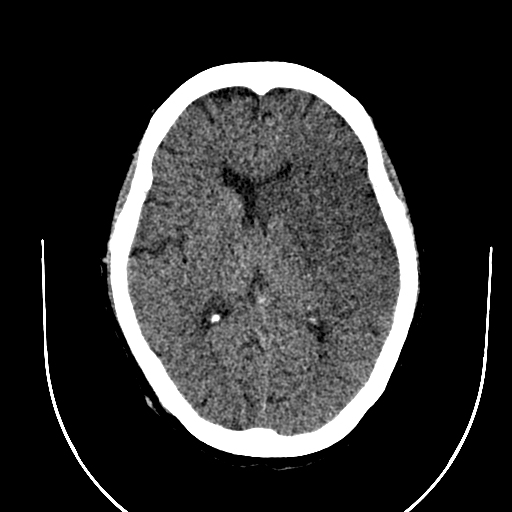
Left frontoparietal and temporal as well as left basal ganglia hypodensity, non-enhancing on arterial phase with loss of grey-white differentiation and effacement of the sulci. There is effacement of the ipsilateral lateral ventricle.
There is focal linear hyperattenuation along the proximal left MCA (hyperdense MCA sign) seen as a filling defect on arterial phase. There are also focal area of hyperdensities in the distal MCA branches which have filling defects on arterial phase.
Case Discussion
The middle cerebral artery territory is most commonly affected territory in cerebral stroke due to the size of the territory and direct flow from the internal carotid artery.
Hyperdense MCA sign refers to focal hyperattenuation of the MCA on non-contrast brain CT due to intraluminal thromboembolic material and is an earliest sign of MCA infarction.
The sensitivity of hyperdense MCA sign is only about 30% but it's specificity is around 90%.
In our case, the presence of intraluminal filling defects on arterial phase confirms the presence of thromboembolic material in MCA.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.