Presentation
Attacks of left facial pain and numbness
Patient Data


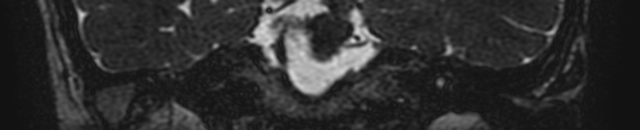







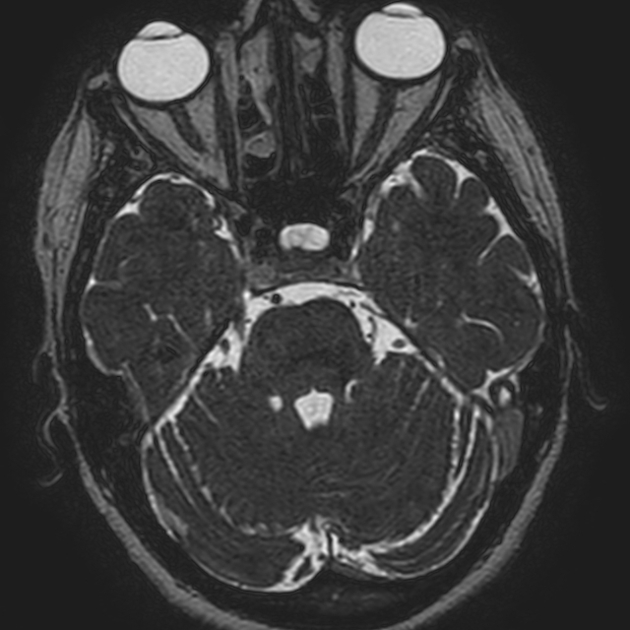
There is compression of the root-entry zone of the left trigeminal nerve by the left superior cerebellar artery. Otherwise, the trigeminal nerves are normal in calibre and signal intensity.
Normal right trigeminal nerve. No posterior fossa or Meckel's cave masses. No evidence of demyelination, brain stem lesions or infarction.
Case Discussion
Compression of the trigeminal nerve by the superior cerebellar artery is the most common cause of trigeminal neuralgia (about 90 %), followed by compression by anterior inferior cerebellar artery and basilar artery.
It is believed that only compression at root-entry zone and proximal cisternal part of the nerve where the nerve is covered by central myelin derived from oligodendrocytes is responsible for trigeminal neuralgia due to vascular compression, while the distal peripherally myelinated (Schwann cells) nerve is not responsible for this entity.
Other causes of trigeminal neuralgia include multiple sclerosis, CP angle masses or cysts and perineural spread of tumours.
Most cases of trigeminal neuralgia are unilateral with right side affected more commonly.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.