Presentation
Neck swelling and pain for two weeks are associated with right hemiface swelling, dysphagia, and dyspnea.
Patient Data
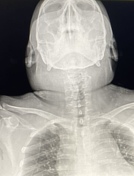
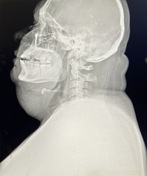
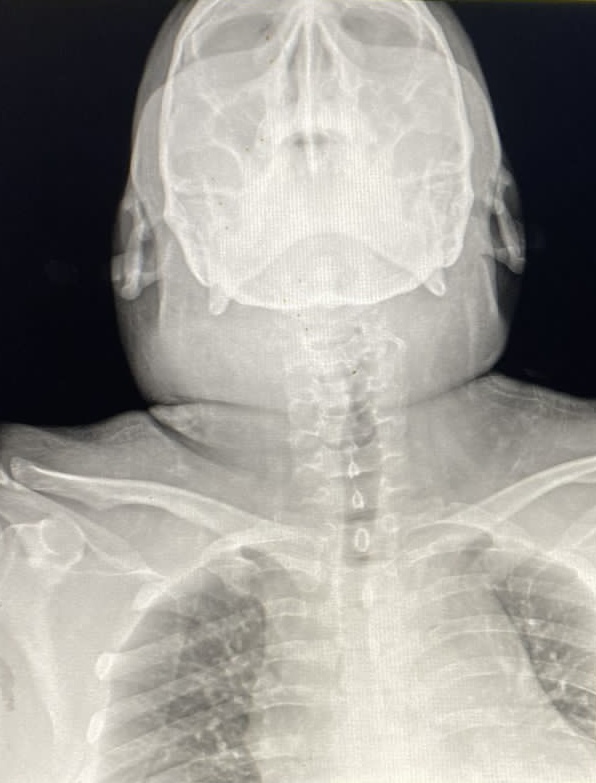
An increase in the size of the right hemineck is observed in contrast with the contralateral neck secondary to soft tissue edema.
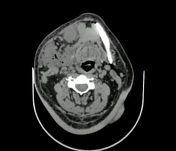

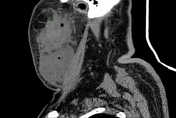

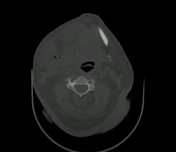

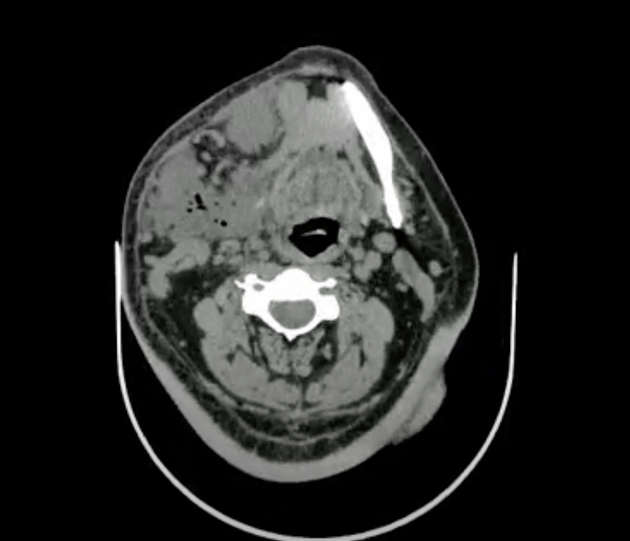
In the soft tissue window on the right side of the neck, there is a large collection with gas focus inside, which is compatible with an abscess. This extends to the suprahyoid level in the masticatory, submandibular, sublingual, and submental spaces; it causes a mass effect in the respiratory tract ipsilaterally.
In association, perilesional soft tissue edema and multiple enlarged inflammatory lymph nodes are observed.
Pus culture isolates Staphylococcus aureus methicilin-resistant
Case Discussion
CT features are compatible with Ludwig angina, complicated by multiple sites of abscesses, including masticatory, submandibular, sublingual, and submental spaces. These abscesses have resulted in partial compression of the airway and oropharynx, causing dysphagia and dyspnea.
Empirical antibiotic therapy was started with piperacillin, tazobactam, and vancomycin. The patient was taken to the operating room to have an incision and drainage for abscesses, as well as vigorous intravenous therapy.
The etiology is usually due to dental infections. Staphylococcus aureus is associated with immunocompromised patients. The patient has a background history of poorly controlled diabetes mellitus.
Co-authors: Alvarez Joselyn Aracely, MD, internal medicine resident. De León Dina Stephanie, MD, radiology resident. García María Fernanda, MD, internal medicine resident.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.