Presentation
Presented with left maxillary and intra-orbital swelling. Initially presented to the dentist. Tumour or infection?
Patient Data
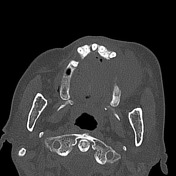

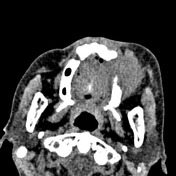

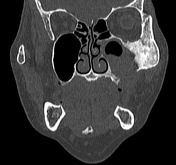




Large mass centred on the left alveloar ridge occupying nearly the entirety of the left maxillary sinus.
Gross destruction of the roof, anterior and lateral walls and floor of the left maxillary sinus. The left inferior orbital wall is destroyed. The mass extends anteriorly into the premaxillary soft tissue, superiorly through the orbital floor to the lateral extraconal space and buccal space. No extension into the masticator space or intracranially.
The floor of the anterior cranial fossa is intact.
Sclerosis of the maxilla extending to the frontozygomatic syndesmosis.
The paranasal sinuses and nasal canal are normal.
Case Discussion
Biopsy of the left maxilla: Squamous cell carcinoma
The differential for this case would be between a sinus squamous cell carcinoma or a sinonasal adenocarcinoma. The nasal cavity is uninvolved making this less likely.
Squamous cell carcinomas most commonly occur from the alveolar ridge of the maxilla.
Head and neck pathology is often very 'space orientated' in terms of the chief differentials. It is also important to identify if the disease process is trans-spatial.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.