Presentation
Acute left side weakness.
Patient Data


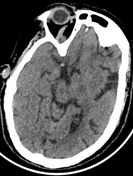
Hyperdense right middle cerebral artery (MCA) with loss of the insular ribbon sign. Also, there is loss of gray/white matter differentiation at the right temporoparietal region with effaced cortical sulci.
Senile involutional changes.
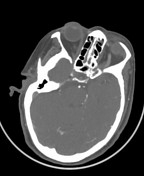


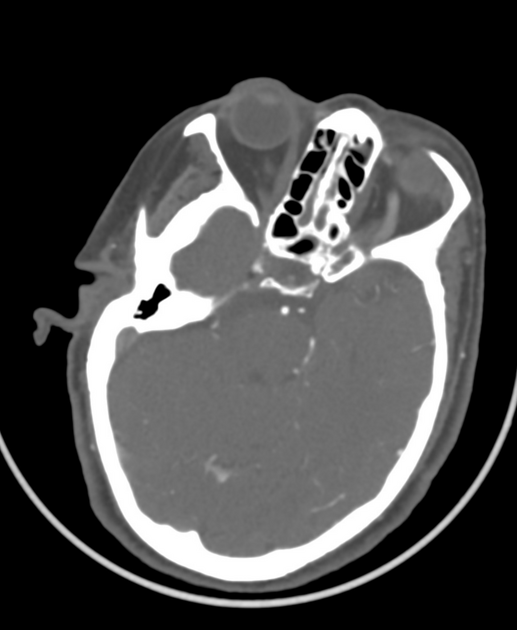
Non-opacified M1 and M2 segments of the right MCA consistent with thrombosis.

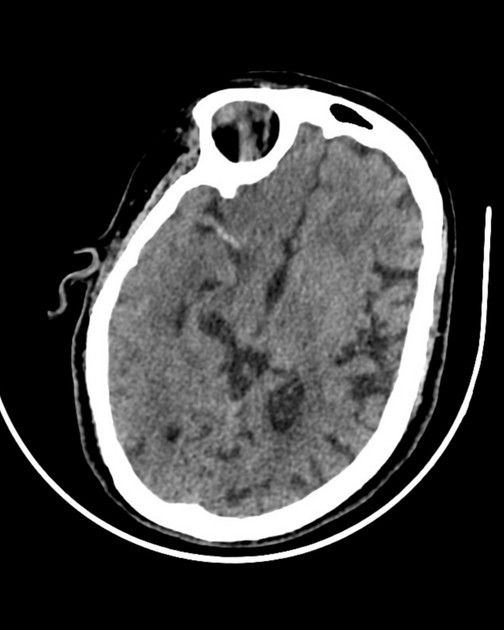
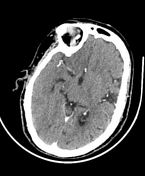
The right cerebral hemisphere appears near totally hypodense apart from basal nuclei with involvement of MCA, ACA, and PCA territories (mostly due to transtentorial herniation with vascular compression), causing significant mass effect in the form of effaced cortical sulci, compressed right lateral ventricle, and significant left-sided midline shift with subfalcine herniation.
Case Discussion
MCA territory infarction refers to a stroke that occurs in the area of the brain supplied by the middle cerebral artery (MCA). The MCA is one of the major arteries supplying blood to the brain, and its territory includes critical regions such as the lateral aspects of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes, as well as parts of the internal capsule and basal ganglia.
Radiological features consistent with right middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory acute infarction.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.