Presentation
History of flu-like illness followed after a few days by headache, fever, seizures and right hemiplegia.
Patient Data
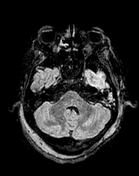

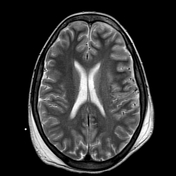

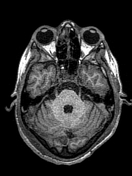



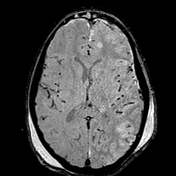

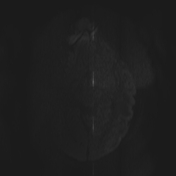

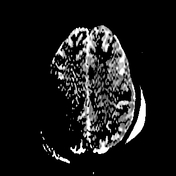

Brain MRI depicts extensive leptomeningeal and pachymeningeal enhancement along the left cerebral hemisphere, and to a lesser extent, along the right frontal convexity, highlighting the presence of sparse subdural collections next to the changes, the most evident in the anterior frontal convexities, with slight restriction to water diffusion probably related to empyemas.
Areas of cortico-subcortical signal alteration were observed next to the affected gyri, including zones of cortico-subcortical enhancement, suspicious for extensive areas of cerebritis.
Diffuse prominence of the leptomeningeal circulation next to the cerebral hemispheres.
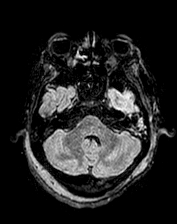
Mucous thickening of the frontal, sphenoid and right maxillary sinuses is observed, with accumulation of secretion mainly in the right frontal, right maxillary and right sphenoid sinuses, suspicious for inflammatory sinusopathy.
Accumulation of secretion in mastoid cells bilaterally.
Case Discussion
The aforementioned set of findings primarily suggests lepto and pachymeningitis complicated with subdural empyema and extensive cerebritis, probably of sinus aetiology.
The biochemical study of the liquor demonstrates an increase in lactic dehydrogenase, an increase in total proteins and an increase in leucocytes (at the expense of polymorphonuclear cells).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.