Presentation
Initially presenting with dysphagia. Unremarkable clinical exam and upper GI fluoroscopy.
Patient Data


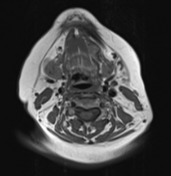

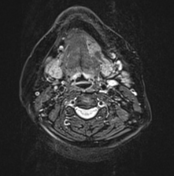

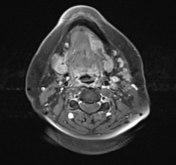

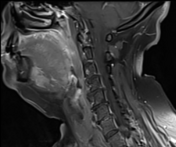

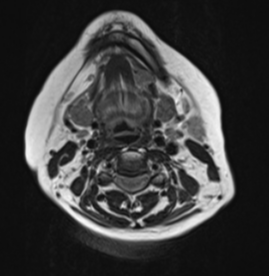
On these selected MR images of the neck, a wide left-sided defect is observed in the mid portion of the left mylohyoid muscle. The left sublingual gland appears to be protruding through this defect into the left submandibular space. It otherwise exhibits normal signal intensity and patterns of enhancement.
No salivary gland masses.
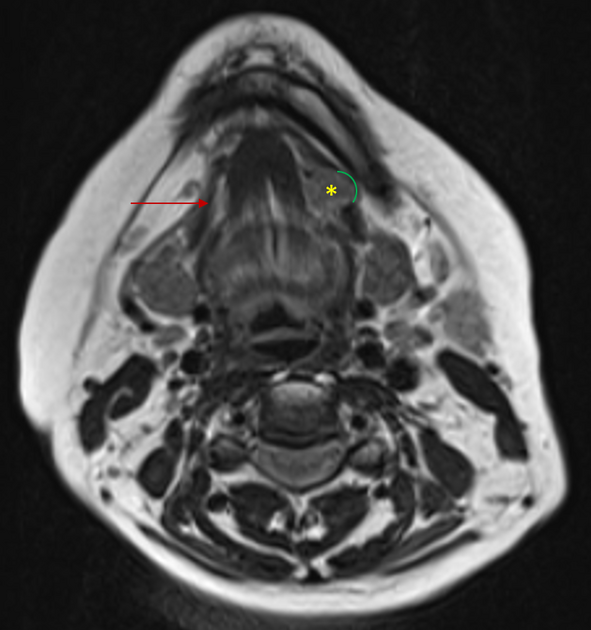
Annotated axial T2-weighted image:
Normal right mylohyoid muscle fibers (red arrow)
Left mylohyoid muscle fiber defect (green arch)
Left sublingual gland (yellow asterisk)
Case Discussion
The mylohyoid muscle is a paired muscular sling forming the muscular floor of the mouth, separating the sublingual and submandibular spaces, which normally communicate posterior to the mylohyoid muscle 1,2.
Normal focal defects (mylohyoid boutonniere) 1 are often present in the mylohyoid muscle, which can result in protrusion of the contents of the sublingual space into the submandibular space, as in this case.
This finding was incidentally discovered and deemed unrelated to patient's presentation of dysphagia.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.