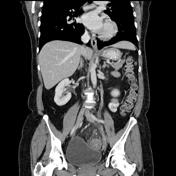
Ovarian vein thrombosis and sigmoid diverticulitis
Updates to Case Attributes
This patient has a history of previous appendectomy and extirpation extirpation of the uterus.
Ovarian vein thrombosis is an uncommon but potentially serious disorder. It arises arises out of the coincident conditions of venous stasis and hypercoagulability, which are commonly present in the recently postpartum patient. Other conditions that are associated with hypercoagulabilityhypercoagulabilities, such as recent surgery, malignancy, and Crohn disease, also increase the patient's risk for ovarian vein thrombosis.
In this case, the thrombosis of the left ovarian vein is likely to be caused by a concurrent sigmoid diverticulitis adjacent to the left ovarian vein vein. Vessel wall abnormalities occur during acute inflammation due to sticking and emigration of leukocytes, and the resultant exposed subendothelial collagen activates platelets leading to thrombosis.
-<p>This patient has a history of previous appendectomy and extirpation of the uterus.</p><p>Ovarian vein thrombosis is an uncommon but potentially serious disorder. It arises out of the coincident conditions of venous stasis and hypercoagulability, which are commonly present in the recently postpartum patient. Other conditions that are associated with hypercoagulability, such as recent surgery, malignancy, and Crohn disease, also increase the patient's risk for ovarian vein thrombosis. </p><p>In this case the thrombosis of the left ovarian vein is likely to be caused by a concurrent sigmoid diverticulitis adjacent to the left ovarian vein. Vessel wall abnormalities occur during acute inflammation due to sticking and emigration of leukocytes, and the resultant exposed subendothelial collagen activates platelets leading to thrombosis.</p>- +<p>This patient has a history of previous appendectomy and extirpation of the uterus.<br><br>Ovarian vein thrombosis is an uncommon but potentially serious disorder. It arises out of the coincident conditions of venous stasis and hypercoagulability, which are commonly present in the recently postpartum patient. Other conditions that are associated with hypercoagulabilities, such as recent surgery, malignancy, and Crohn disease, also increase the patient's risk for ovarian vein thrombosis.<br><br>In this case, the thrombosis of the left ovarian vein is likely to be caused by concurrent sigmoid diverticulitis adjacent to the left ovarian vein. Vessel wall abnormalities occur during acute inflammation due to sticking and emigration of leukocytes, and the resultant exposed subendothelial collagen activates platelets leading to thrombosis.</p>
Updates to Study Attributes
CT demonstrates multiple sigmoid colon diverticula with surrounding mesenteric fat stranding. These findings are compatible with diverticulitis. On the left lateral side of the left ovariansigmoid colon, a dilated venous structure is seen with an endoluminal round thrombus. This vein
Image CT (C+ portal venous phase) ( update )

Image CT (C+ portal venous phase) ( update )