Presentation
Motorcycle accident. Polytrauma patient. Pubic symphysis and lumbosacral pain.
Patient Data
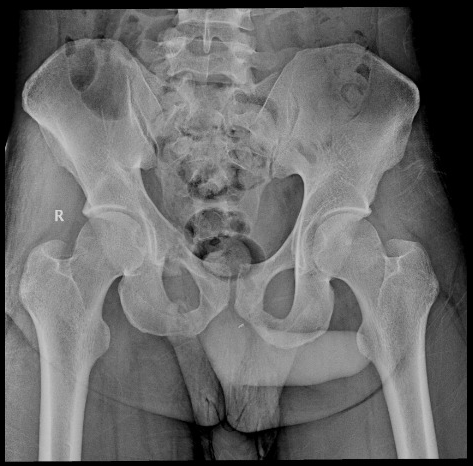
Radiograph of the pelvis revealed a superior and inferior right pubic rami fracture. Diastasis of the right sacroiliac joint was questioned and a CT was performed to proceed on clinical investigation.
There is an artifact below the pubic symphysis, it is not a foreign body and was present in most exams performed that day.
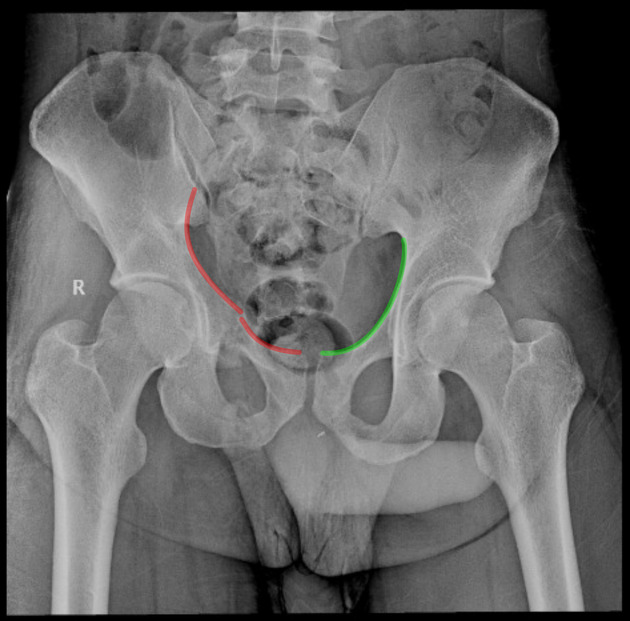
The iliopectinal line is drawn bilaterally. On the right, the line drawn in red is interrupted, a sign of pelvic ring fractures which may be present in acetabular fractures and superior pubic rami fractures, for example. On the left, the line is drawn in green is uninterrupted.
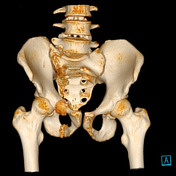
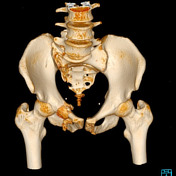
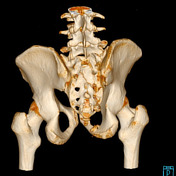
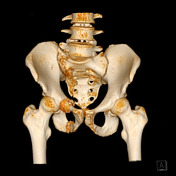
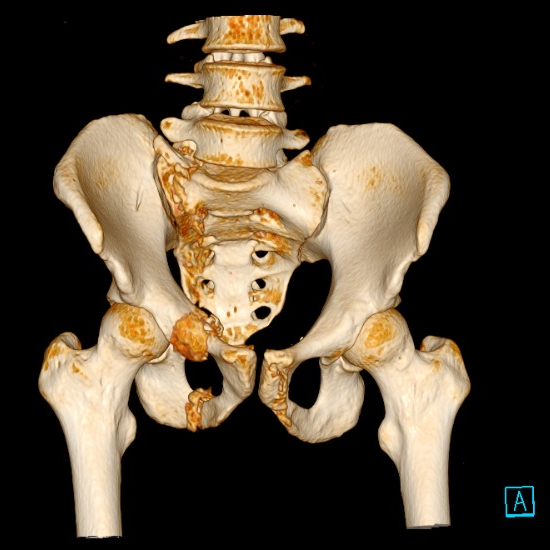
The 3D reconstruction of the CT exam allows for better visualisation of the superior and inferior right pubic rami fracture. There was no diastasis of the right sacroiliac joint. However, the exam revealed a sacral fracture (Denis-type I).
Case Discussion
Pubic rami fractures are a subgroup of pelvic fractures. Pelvic fractures are related to pelvic trauma with a risk of grave haemorrhage. If a pelvic fracture is suspected, proper physical examination and radiographic studies are extremely important.
The initial radiograph performed on this case raised suspicion of a right sacroiliac joint injury. A CT was performed, which revealed a sacral fracture. There are many important neurovascular structures in this region that may be injured due to pelvic trauma. In the present case, the patient did not present neurologic deficit of L5 nor S1 roots.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.