Presentation
Sudden headache accompanied by visual impairment.
Patient Data
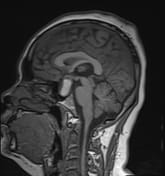

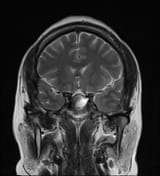

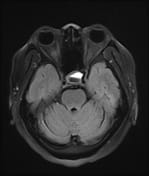

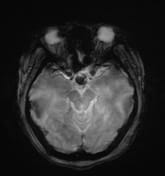

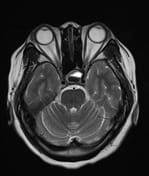

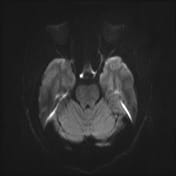

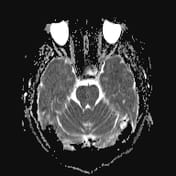

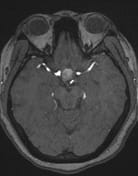

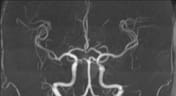
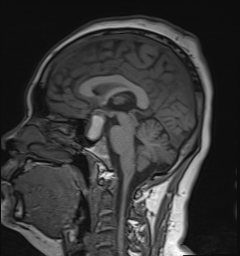
A cystic mass in the pituitary region, measuring approximately 28 × 17 × 15 mm, with an irregular thick wall and an internal fluid-fluid level on T2W/FLAIR. The lesion demonstrates intrinsic high signal intensity on T1W and low signal intensity on GRE (consistent with hemorrhage). There is suprasellar extension with compression of the optic chiasm.
No vascular abnormalities detected on MRA.
Case Discussion
The imaging findings are consistent with a pituitary region mass with internal hemorrhage (intrinsic high T1 signal and fluid-fluid level), with an irregular thick wall, and clinically suggestive of pituitary apoplexy. To date, the most common etiology remains a cystic pituitary macroadenoma.
It is important to note that pituitary apoplexy is not a radiological diagnosis. Pituitary hemorrhage is, but apoplexy requires the correct clinical context (sudden onset of neurological symptoms and signs ascribed to the mass) which are present in this case.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.