Post ERCP pancreatitis
Updates to Case Attributes
Acute pancreatitis occurs in approximately 5% of diagnostic procedures and 10% of therapeutic procedures. A commonly used definition of post-ERCP pancreatitis is abdominal pain for more than 24>24 hours after the procedure and levels of serum pancreatic enzymes three times above normal. This definition excludes the 30%–75% of patients who are asymptomatic and have an elevated amylase level alone. Asymptomatic hyperamylasemia peaks 90 minutes to 4 hours after ERCP and resolves within 48 hours.
-<p>Acute pancreatitis occurs in approximately 5% of diagnostic procedures and 10% of therapeutic procedures. A commonly used definition of post-ERCP pancreatitis is abdominal pain for more than 24 hours after the procedure and levels of serum pancreatic enzymes three times above normal. This definition excludes the 30%–75% of patients who are asymptomatic and have an elevated amylase level alone. Asymptomatic hyperamylasemia peaks 90 minutes to 4 hours after ERCP and resolves within 48 hours. </p>- +<p>Acute <a title="Pancreatitis - acute" href="/articles/acute-pancreatitis">pancreatitis</a> occurs in approximately 5% of diagnostic procedures and 10% of therapeutic procedures. A commonly used definition of post-ERCP pancreatitis is abdominal pain for >24 hours after the procedure and levels of serum pancreatic enzymes three times above normal. This definition excludes the 30%–75% of patients who are asymptomatic and have an elevated amylase level alone. Asymptomatic hyperamylasemia peaks 90 minutes to 4 hours after ERCP and resolves within 48 hours.</p>
Tags changed:
- pancreas
- ercp
- iatrogenic
Updates to Study Attributes
Pancraetic head is minimally hypodencehypoattenuating, but not enlarged. Fat strandingThere is observedfat stranding in the peripancreatic fat.
Peripancreatic and right perirenal fluid collection is seencollections. There is also free fluid in the right paracolic, subhepatic (Morrison' pouch(Morison pouch), right subphrenic an, and pelvic spaces.
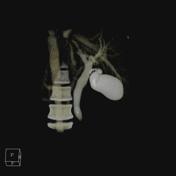
Gallbladder and extra and intrahepatic biliary ducts are filled with contrast whcihwhich is due to its use during ERCP. This allowed me to make a 3D reconstruction from the biliary tracts.
Image CT (C+ arterial phase) ( update )
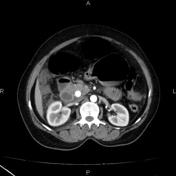
Image CT (3D reconstruction) ( update )