Presentation
Drowsiness, seizures, and a severe headache with a hypertensive emergency
Patient Data
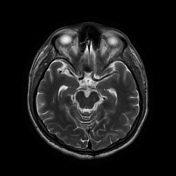

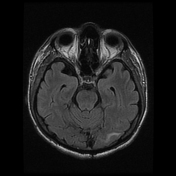

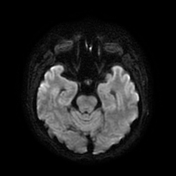

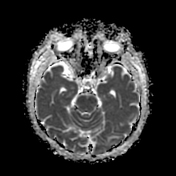

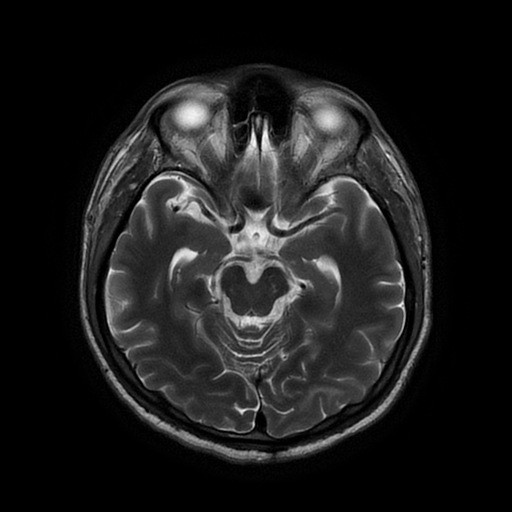
Areas of increased signal intensity are seen in the left subcortical cerebral hemisphere, both frontoparietal and temporal in location. They are displaying high signal intensity on FLAIR and T2-weighted images.
They also display a non-restricted diffusion pattern with a hypointense signal on DWI and an increased signal on ADC images.
Case Discussion
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a clinical syndrome characterized by typical neurological symptoms more commonly in patients with hypertension, supported by neuroimaging evidence of vasogenic edema localized to the posterior cerebral white matter. While the edema is usually bilateral, isolated involvement of one cerebral hemisphere can be seen, as well as involvement of the frontal lobe and cortex.
The patient was treated for hypertension and received anti-seizure medications. A follow-up MRI was scheduled after 3 weeks.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.