Presentation
Right progressively enlarging breast mass.
Patient Data
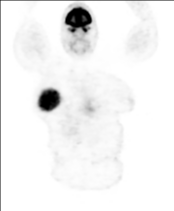



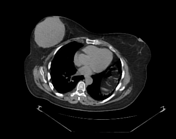

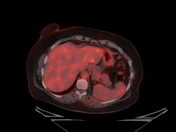

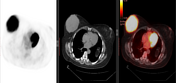
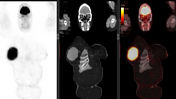

Right UOQ retroaerolar large well circumscribed breast mass which measures 10.1 x 9.3 x 11.0 cm along its max TS, AP, and CC dimensions. It shows FDG avid uptake with SUV max 15.
Mild increased FDG uptake by a few mildly enlarged right axillary lymph nodes with the largest measuring 8 mm in the short axis with SUV max 1.3.
No other FDG avid neoplastic lesions all over the body.
Nature of specimen: Tru-cut biopsy
Gross examination:
one greyish-white tissue core measures 1.5 cm long, totally submitted.
Sections prepared from paraffin block for immunostaining using Bench Mark UL TRA system for CD20, CD3, CD10, BCL6 and Mum-1, CD20 clone (L26), CD3 Clone (2GV6), CD10 clone (SP67), BCL6 clone (G/191 E/A8), and Mum-1 clone (EP190).
Microscopic examination:
The examined sections form the received material revealed a core of lymphoid tissue with atypical lymphoid infiltrates formed of small and intermediate cells with scattered large cells.
*IPT (Positive control showed appropriate reactivity).
CD20: Diffuse strong positive.
D3: Positive in reactive lymphoid cells.
CD10: negative.
BCL6: scattered positive cells.
Mum-1 scattered positive cells.
Diagnosis:
Right UOQ breast mass, Tru-cut biopsy.
Findings are compatible with malignant B cell lymphoma.
Case Discussion
The patient presented with a large breast mass that showed avid FDG uptake. The mass's size and well-defined margins were not typical of breast carcinoma; instead, they were more suggestive of other breast masses that could have caused the giant size, such as phyllodes tumours, medullary breast carcinoma, or primary breast lymphoma. We suggested malignant phyllodes, but the pathology revealed breast lymphoma, which, when combined with the PET scan's lack of systemic lymphoma throughout the body, would have led to the diagnosis of primary breast lymphoma.
Primary breast lymphoma is typically a B cell type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), with the most common histologic type being diffuse large B cell lymphoma, as in our case.
For a tumour to be labelled as a primary breast lymphoma, it must fulfil the following criteria:
the disease should be in the breast or in close proximity to breast tissue
no previous history of extramammary lymphoma
no evidence of widespread disease, except ipsilateral axillary lymph nodes may be involved if developing simultaneously with primary breast tumour
Breast lymphoma most commonly appears as a solitary mass.
Differential diagnosis for giant breast mass considers whether a mass is well-circumscribed or ill-defined and the presence of fat.
well-circumscribed masses with fat include lipomas and hamartomas
well-circumscribed masses without fat include cysts, haematomas, giant fibroadenomas, phyllodes tumours, and malignant masses such as medullary carcinoma or primary lymphoma
ill-defined masses include breast carcinoma and abscesses




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.