Presentation
HIV-positive patient presents with dysuria, fever and pelvic pain. Referred for a prostate MRI after an initial ultrasound.
Patient Data
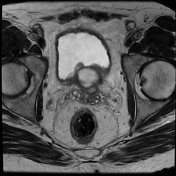

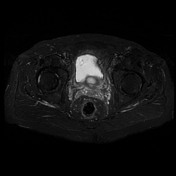


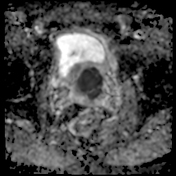

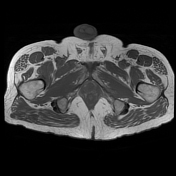

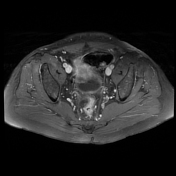

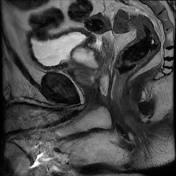

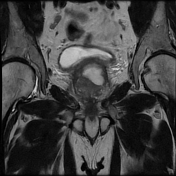

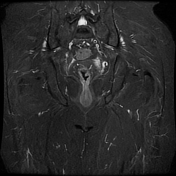

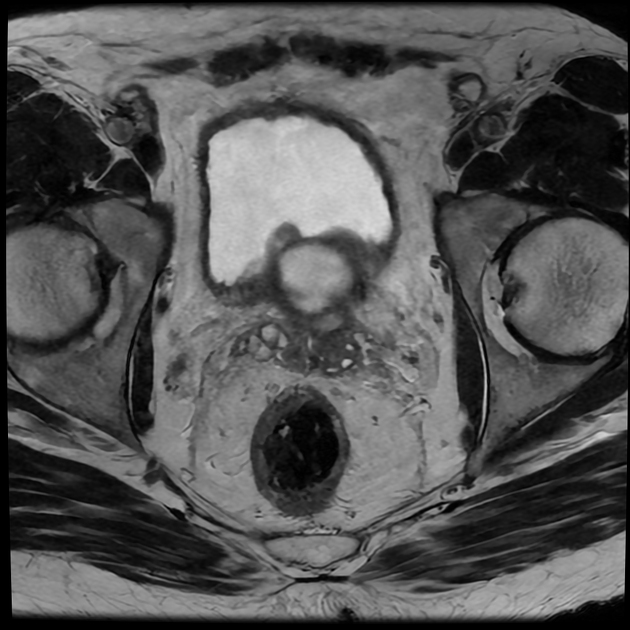
The prostate measures 6.2 x 5.2 x 5.0 cm (cc x w x AP) with an estimated prostate volume of 88 cc.
A multi-septated prostatic abscess involving the left anterior and posterior transitional zone from base to mid gland measuring 3.4 x 4.2 x 4.6 cm (cc x w x AP). There is well-identified diffusion restriction and associated reduced ADC mapping. There is peripheral enhancement and intralesional septal enhancement.
There are bilateral heterogeneous nodules throughout the transitional zones with a pedunculated impression on the bladder base. Features consistent with BPH and PIRADS 2.
There are no occult bone lesions, suspicious loco-regional lymph adenopathy, or normal seminal vesicles
Case Discussion
An example of a multiseptated, ring-enhancing, prostatic abscess in an HIV-positive patient.
Tuberculous prostatitis and tuberculous abscess need to be excluded given the known immunosuppression and a normal PSA at 0.54 ng/mL (0.0- 4.0ng/mL, normal range). In this instance, the work-up proved negative and E.Coli was cultured.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.